In ancient times, people used the potential of the soil differently than modern farmers. The field was divided into parts and each of them was sown according to a special pattern. Nowadays, such a technology for restoring soil with minerals and vitamins is impossible for certain reasons.
This means that there is a need to use additional means: fertilizing, mineralization, and the addition of individual preparations. Potassium sulfate is a substance that is used as a fertilizer. With its help, you can replenish the necessary elements to normalize the growth and development of vegetable, berry and other crops.
Description and characteristic properties of the fertilizer
K₂SO₄ or potassium sulfate is a popular product in agriculture. The chemical formula indicates a high concentration of components that are extremely important for cultivation. These minerals are obtained from natural components:
- chenita;
- langbeinite.
Use in a country house, field, or greenhouse is allowed, as it brings benefits in open and closed ground. It looks like crystals. The color is light. Can be purchased in several forms:
- powder;
- granular;
- liquid
In all forms, the composition and chemical properties will be preserved. When purchasing potassium sulfate, agricultural technicians pay attention to the manufacturer’s instructions and instructions. The main condition for an agricultural product: the content of the main element is at least 45-50%.
Composition and principle of action of the substance
Potassium sulfate is an important component for plants. There are GOST standards, according to which the composition of the fertilizer is checked. So, in addition to the main element, potassium, any type of product must contain:
- sulfur;
- iron;
- sodium.
If the drug is used for laboratory purposes, it contains arsenic. You can work with potassium sulfate calmly and fearlessly. Unlike similar fertilizers, it does not contain chlorine, which is poorly tolerated by most plants.
The agrochemical is used for certain purposes. The entry will be useful if necessary:
- feed in the autumn before winter frosts. The drug will provide protection during the wintering period, preserves the viability of heat-loving crops;
- percentage increase in the presence of sugar and vitamins in all parts of the plant (fruits, shoots);
- crystals reduce the risk of infection with fungal diseases. Including gray rot;
- feed plants for which chlorine is difficult to tolerate. And also to increase the yield of citrus fruits and legumes, grapes and potatoes.
Granular potassium sulfate, just like in liquid or powder form, will improve microcirculation in plant tissues. This makes it possible to distribute equally important nutrients without hindrance.
Thanks to the juice, the balance of growth during the growing season, improvement and development of the root system is maintained. Plant growth is also stimulated. Culture stimulation will be most productive if applied in liquid form.
What is the difference between potassium sulfate and potassium sulfate?
These are different names for the same substance and fertilizer. There is no difference if you purchase fertilizers under these names - their purpose, dosage and consumption will be the same.
Potassium sulfate is a widely used fertilizer; it is used both in fields and in private gardens, as well as for feeding indoor flowers. Does not contain chlorine, therefore it is approved for use for all crops. Fertilizer increases the content of vitamins and carbohydrates in the products obtained from plants fed with it.
When feeding fruit and berry plants in early autumn, they overwinter better. It can also be used for replenishment in the spring and throughout the season, at certain intervals. Potassium sulfate does not contain chlorine, so it is often chosen for feeding crops that do not tolerate it: grapes, nightshades, citrus fruits. Sulfur will be useful for crops from the legume and cruciferous families.
After fertilizing with potassium sulfate, the quality of the fruits, their taste, and the amount of sugars, starch, and vitamins they contain improves. They become more resistant to rot and other infections that spoil fruits in storage.
Efficiency of use for plants
The fertilizer composition helps young seedlings and plants go through the rooting stage twice as fast. But besides the positive aspects of use, there are also negative side effects. They refer to the combination of potassium with certain types of substances.
Potassium nitrate should not be used during fruit ripening or after with urea. Some sources indicate chalk. Such fertilizing preparations contain nitrogen. Potassium and nitrogen create unfavorable conditions for plant development.
Important! If the soil is acidic, then potassium sulfate can be used with slaked lime. Before use, you should check the compatibility of the two components on a small plot of land.
The negative side of using potassium nitrate is the absorption of magnesium, manganese and calcium. These microelements help plants develop faster. But sulfate inhibits them, which harms the crop. Additional addition of substances to the soil will be required.
General recommendations
Potassium fertilizer is important and necessary for the normal development of plants. The addition of the substance provides protection from diseases, strengthens the immune system, and makes it possible to quickly get used to the open ground during transplantation.
It is recommended to apply fertilizer not only for young animals. The benefits will be obvious when planting shrubs, grapes, and young trees. For adult crops, potassium sulfate is also needed and important.
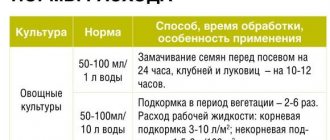
Instructions for use indicate the nuances of use, dilution and application of fertilizer. To obtain a high yield, gardeners plan to apply potassium sulfate in advance.
In addition to taking into account the dosage and type of soil, it is worth considering that fertilizing must be timely. The gap between applications, the possibility of combining with other organic preparations and chemicals. K₂SO₄ during growth brings not only benefits, but also harm.
What is the deadline for payment?
Potassium nitrate should become available to the roots. Therefore, a different scheme is used for seedlings than for adult plants. The most suitable time for fertilizing the soil is autumn. Before this, the top layer of soil is removed (approximately 20-30 cm).
The number of plots to be removed depends on the name of the crop. After application, the area is backfilled. In spring, the young plant will take root much faster. At the same time, sprouts and seedlings are protected from bacteria and fungal spores, which gain strength over the winter.
Adult, perennial plants are fed using pits (vertical holes). They are made at a 45-degree angle aimed at the root system. The dosage corresponds to the name and age of the plant. The agrochemical is poured.
Analogs
Potassium sulfate can be replaced in the garden with various potassium fertilizers, for example, potassium chloride and chlorine-free substances - potassium nitrate, potassium magnesium. They contain potassium in different percentages and also include other elements. In private households, potassium sulfate can be replaced with ash, which will become not only a source of potassium, but also other elements. Only the ash left from burning wood and plant residues is suitable for feeding. Coal coal is not suitable.
Features of fertilizing
Application methods are interconnected with the feeding period. The use of potassium sulfate is allowed not only in liquid form, but also in dry form. Both options occur in the same way - using a furrow.
Trenches are dug around trees depending on their age. The volume of liquid also varies depending on the age and name of the crop: 100-200 g. The crystals should be buried in the root zone in loose soil.
In liquid form, adding potassium is easier. Dissolve in the required amount of water. Place it into the prepared trench. Cover with soil. The methods are chosen by the farmer himself. The liquid form is most often used, since the fertilizer is absorbed more quickly by the roots.
Spraying is allowed. Granules (30-40 g + 10 l) are stirred until completely dissolved. Spraying occurs using a spray bottle. Part to be processed: trunk, leaves. The calculation of the substance occurs in such a way that there are no residues.
In the garden
The use of fertilizer in the garden is necessary as protection against diseases and plant growth/development. Suitable for:
- cucumbers;
- cabbage and potatoes;
- carrots and beets;
- potassium for tomatoes is a definite help for speeding up and eliminating empty flowers.
Dosage for cucumbers and tomatoes – 15-20 g per 10 liters. For other crops, the dose increases to 40 g.
In gardening
Gardening is one of the milestones in the development of agriculture. Strawberries and raspberries require less potassium (15-20 g) than fruit trees (calculated per planting hole). In the standard application for shrubs and trees, 100-200 g will be required per root system.
Potassium sulfate is also necessary for vineyards. They bring it between the rows. The depth of the trench is up to 8-10 cm. The moment of application is before the inflorescences appear. Method: liquid working mixture.
For flowers
For roses and hydrangeas, potassium sulfate is needed no less than feeding grapes. The method for better protection is a liquid mixture. Application periods: spring and autumn. Use should be rational, if necessary. Suitable for ornamental plants, indoor flower beds.
Dilute humate in the same way as for feeding cucumbers: add at least 15 g per 10 liters of water. During rot epidemics - 20 g. The benefits will be obvious on all soils (see above).
Important! Potassium sulfate is applied exclusively to each bush, tree or shrub. This feature persists for all types of crops. Possible spraying. But this technique is used for flower beds and densely planted plants (strawberries, wild strawberries or raspberries).
Indications for use on different soils
Replenishes potassium deficiency and nourishes the following types of soil:
- soddy-podzolic soils containing up to 5-7% humus;
- peat soils;
- chernozem - when growing root crops, vegetables, sunflowers, fruit trees and shrubs (crops consume sodium and potassium in large quantities);
- steppe zones - gray soils and chestnut soils;
- acidic soils provided that lime is used.
Toxic properties
The hazard class of potassium sulfate is very low, as it is permissible to eat. At the same time, we cannot forget that this chemical compound is impossible. An excess of agrochemicals leads to disruption of the digestive system and deterioration of the plant’s immunity.
It also takes into account the fact that the composition may contain additional microelements that are needed by the culture, but can be harmful to human health. To protect yourself from exposure to chemicals, use a protective suit, goggles and a respirator. In case of contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the working solution or dry powder: the damaged areas are treated.
It is not allowed to increase the recommended doses. The drug is not highly toxic, but an excessive dosage contributes to the death of plant parts. Rescue procedures are labor-intensive and fail in 45% of cases.
Alternative to the drug
Potassium sulfate is an ideal fertilizer for all types of crops and plants. But if necessary, it can be replaced with alternative substances of organic and chemical origin. The first substitute was wood ash. It contains more than 15% potassium. In second place is potassium magnesia. It is practically no different from saltpeter. The composition included:
- magnesium – up to 9%;
- potassium – up to 3%.
This substance is used as a substitute for light soils. Can be replaced with potassium sulfur, salt or potassium carbonate. Potassium chloride is often used.
60% of gardeners buy it, since the calculation is made not for plant bushes, but for square footage. It's more economical. All fertilizers are diluted in water and are available in agricultural stores.
Storage rules
Storage of sulfate is stored in a dry place. Since the substance is not explosive, temperature conditions do not affect safety. It is still advisable to avoid overheating, moisture, and dust.
The prepared working solution of potassium sulfate cannot be stored. Therefore, it is calculated strictly according to the cultivated area and the number of plants. It is recommended to buy the powder in dry form for the season. Sales are made in bags of 500 g. Maximum volume – 5 kg.
After the expiration date, sulfate should not be used. The chemical composition loses its positive abilities. If the substance gets wet during storage or use, the sulfate changes its structure and formula, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of the soil.
Safety precautions
Potassium sulfide must be added in compliance with safety regulations. That’s why it’s so important to use personal protective equipment – a mask or respirator, goggles, gloves. This must be done regardless of the method of application of the product, which is applied in dry or dissolved form.
Protective agents help prevent the substance from getting on the skin and mucous membranes. They also protect the respiratory organs from toxic fumes and dust. After finishing work, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap.