Author of the article
Daria Vorontsova
Reading time: 29 minutes
AA
I collected bit by bit information about phytolamps from various sources to write this article: how to choose a phytolamp for seedlings, how to use lighting devices correctly so that the seedlings are strong and healthy. After reading the article, you will have a piece of my personal experience and mistakes, as well as complete information about the types of phytolamps and their use. The rating, based on reviews from experienced gardeners, will help you decide on the most suitable device.
Why do you need additional lighting for seedlings?
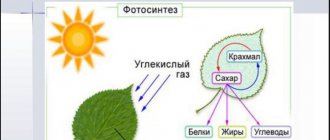
In order for a plant to develop harmoniously, it needs natural light.
Lack of ultraviolet radiation leads to reduced seedling growth and withering of shoots. The sprouts that have barely hatched are thin and look weak and lifeless. The greatest deficit of sunlight occurs in January – March. It is at this time that the sowing of seeds for seedlings begins.
Exotic plants also need additional lighting. The length of daylight hours for them should be at least 12 hours. You can increase the amount of useful radiation using special devices - phytolamps.
A few final tips
- It’s time to add additional light to an indoor flower if it suddenly stops blooming, becomes faded and lethargic, and its leaves are drawn to the window in search of light.
- This is especially true in winter, when the length of daylight hours is halved. At this time, even plants “living” on southern windows require an additional portion of rays.
- For additional illumination, use lamps with a cold glow - fluorescent, gas-discharge, LED.
- Remember: excess lighting is no less harmful than its deficiency. Try not to get carried away; 10–14 hours of additional light is enough for the plant to develop properly.
- Turn on the lamp 1-2 hours before dawn, and turn off 2 hours after dusk. The correct alternation of day and night is the key to the health of your indoor flowers.
What is a phytolamp
The device allows you to obtain a wide spectrum of electromagnetic radiation necessary for the growth and development of the plant. Powered by LED or gas discharge lamps. Using converters and electronic microcircuits, developers create phytolamps with a directed flow of light of a certain, most often red or blue, hue
Types of phytolamps
Depending on the design, the following types of lamps for seedlings are distinguished:
Luminescent
The most affordable lamps. They are very popular among gardeners. They do not emit heat and do not burn seedlings. They emit light in the blue spectrum. The disadvantages are low power and fragility. Flickering lamps are bad for your eyesight.
Mirror
The glass of such lamps is coated with a film of neodymium, which can absorb part of the yellow-green spectrum. The efficiency is significantly lower than that of fluorescent devices. Most often, such lamps are used to illuminate orchids.
Energy saving
They are a type of fluorescent lamps. They do not burn seedlings, have a long service life and low energy consumption. Most often they are used to illuminate individual adult plants.
Sodium
They create a source of red-orange light and contain virtually no blue spectrum. Not suitable for home use due to too much power. Most often they are installed in industrial greenhouses.
LED
They emit a spectrum of light that is most optimal for the growth and development of seedlings. It can be independently adjusted by changing one diode to another. They do not emit heat and do not burn plants. They have a compact shape, the lamps can be used in ordinary household appliances. They have a long service life of up to 50 thousand hours. The lamps are safe for the health of people and animals. The downside is the high cost.
Helpful information
Daria Vorontsova
Amateur gardener. He is interested in growing various greens at home.
When choosing lamps, you should focus on the expected service life. Gas discharge lamps are cheaper, but will not last longer than 1 season. LED lamps are more expensive, but pay for themselves due to their long service life.
What is the difference between a phytolamp and an incandescent lamp?
Plants need blue and red rays to develop. Conventional incandescent lamps emit light in the yellow and green spectrum and do not have a significant effect on vegetative processes. At the same time, they generate a large amount of heat, which can cause burns on the leaves. Incandescent lamps have a short lifespan and high energy consumption.
Phytolamps are designed specifically to stimulate the vegetative processes of plants. They do not emit heat and do not burn the seedlings. The devices are completely fireproof. Complete sealing of the lamp allows it to be used in conditions of high humidity.
Which spectrum to choose
Phytolamps have one spectrum or several at the same time. Such models of phytolights are also called bicolor or multicolor. For plants to grow and develop, they need different light levels.
Multispectral phytolamps operate in three spectra: red, blue and warm white light. They are suitable for growing plants with a thick and dense crown, as well as at the stages of flowering and ovary formation.
Full spectrum phytolamps alternately operate in different ranges with peaks in the red and blue zones. Such phytolamps are excellent for growing seedlings and adult plants indoors without or with insufficient natural light. However, it is worth knowing that in some types of phytolamps their radiation irritates the organs of vision and it is recommended to install them in non-residential premises.
How to use a phytolamp
When using a phytolamp, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The lamp should be placed above the plants, not to the side. Otherwise, fragile sprouts will reach towards the light and bend.
- It is necessary to calculate the installation height of the lamp as accurately as possible. Too close a distance will burn the plant, and too high a position will scatter the light.
When using a phytolamp for seedlings on a windowsill, it is necessary to monitor the sprouts and promptly adjust the height and intensity of lighting. The healthy appearance of the seedlings will indicate that all the necessary parameters have been selected correctly.
The lamp must not be covered with a lampshade, reflector or shade. This can lead to overheating and damage to the diodes. In closed greenhouses and grow boxes, it is necessary to install additional airflow for the emitters.
At what height should a phytolamp be hung?
The recommended distance from the lamp to the seedlings is indicated by the manufacturer on the device packaging. As a rule, it is 20-45cm.
The height of the lamp suspension is calculated from the top of the shoots, and not from the ground or window sill.
For home use, it is recommended to use lamps with reduced wattage. Strong devices can cause burns on plant leaves. To understand whether the height of the suspension is calculated correctly, you need to place your palm under the light source at the level of the seedlings. If a feeling of heat appears within 30 seconds, the lamp needs to be moved higher.
How long should a phytolamp burn?
Before germination, seeds can be illuminated around the clock. After the first shoots appear, illumination with a phytolamp is organized in day-night mode. The optimal mode is considered:
- at 6 am, turn on the lamp for 2.5-3 hours;
- during the day, illumination due to natural daytime sleep;
- at 17 o'clock the lamp is turned on until 22 o'clock.
Helpful information
Daria Vorontsova
Amateur gardener. He is interested in growing various greens at home.
The backlight mode is adjusted depending on the weather outside the window. In cloudy and dark times, the phytolamp can be turned on earlier. On a bright sunny day, reduce the amount of additional lighting.
The lighting mode is also adjusted depending on the crop being grown. For some plants, a day length of 10-11 hours is enough, others need at least 12.
For example:
- tomatoes – 14-16 hours;
- cucumbers – 14-16 hours;
- cabbage – 15 hours;
- peppers – 9-10 hours;
- eggplants – 8-10 hours;
- radishes – 12-15 hours;
- celery – 12-15 hours.
If seedlings are grown on racks in conditions of limited natural light, then the phytolamps are turned on from 7 am to 20-22 pm.
If seedlings are grown on a window on the sunny side of the house, then the lamps are turned on only in cloudy weather.
Groups of plants according to light needs
Based on the amount of light required, indoor plants can be divided into 2 main groups: light-loving and shade-tolerant, content with moderate lighting.
There is also an intermediate group - plants that prefer partial shade. This group includes only some species of light-loving or shade-tolerant genera. A striking example is Aglaonema, the natural species of which grow in forests and are therefore shade-tolerant. However, variegated (“variegated”) varieties prefer diffused light, without which they may lose their original color.
IN THE PHOTO: Variegated Aglaonema does not tolerate light deficits as easily as species with monochromatic leaves
The first group includes desert plants - Sedum, cacti, Haworthia, Hoya, Gasteria, Coleus, Croton, Eucalyptus. The second group includes Ivy, Dracaena fragrant, Saxifraga, Monstera, Aspidistra, Begonia.
You can even determine which group a particular plant belongs to visually. Just take a close look at it. Thus, shade-tolerant species are dark green in color, their leaves are wide, matte, and sometimes quite dense. The shoots of such plants are long, most often thickened. Light-loving species, on the contrary, have light green, equilateral, narrow and shiny leaves, often hard and thin. The shoots are short, with hairs.
IN THE PHOTO: Kleinia loves to bathe in the sun
As for the so-called “shade-loving” species, not a single flowering plant likes shade. But their “younger” brothers (although evolutionarily they are more like “grandfathers and grandmothers”) - mosses, lichens and ferns prefer the shade, because exposure to light can cause burns. Therefore, shade-loving plants are classified as a separate, less common group with their own specific conditions.
You can determine which group of plants your particular flower belongs to by visiting our Encyclopedia. The “Illumination” characteristic is indicated by a “sun” icon. Point it at it and you'll know how much light your plant needs.
Harm of phytolamps to people and animals
- When used correctly, phytolamps are absolutely safe for humans and animals. Fluorescent and mercury lamps may pose a minor hazard. If the flask is damaged, mercury evaporates into the air and can cause poisoning with prolonged exposure. Therefore, damaged lamps must be disposed of immediately.
- If the sodium flask is damaged, vapors of a mixture of mercury and sodium enter the air. With short-term contact they are harmless to humans and animals. With prolonged exposure, vapors can cause exacerbation of chronic diseases. Sodium lamps also need to be replaced immediately when chips or cracks appear.
- LED lamps do not contain vapors of harmful metals and trace elements. At the same time, the lamps emit ultraviolet light. Their use at night can disrupt the production of melatonin, the sleep hormone.
- Inexpensive phytolamps have one significant drawback. The light from such lamps constantly blinks and can cause fatigue and irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes. With prolonged exposure, migraines, decreased visual acuity, and decreased performance may occur.
- Prolonged exposure to blue light can cause blurred vision and fatigue. At night, exposure to blue light causes insomnia.
- When exposed to red spectrum waves for a long time, a person may feel dizzy. Rapid heartbeat and nausea. Red waves can provoke an exacerbation of inflammatory processes and cause burns on the skin.
- Flashing light bulbs can have a negative impact on large pets. Avoid leaving cats and dogs exposed to blue and red light for long periods of time.
- Phytolamps are safe for birds. In livestock farms, infrared lamps are often used to prevent outbreaks of mass diseases.
- But for turtles and other amphibians, the light of fluorescent lamps, on the contrary, is useful. It gives them the necessary amount of heat and ultraviolet radiation. LED lighting is made for aquarium fish.
- To ensure that lighting does not cause problems, it is best to install phytolamps with a power of no more than 80 W at home.
- Reflux halogen lamps contain mirror reflectors and can be used indoors without harm to health.
Which lamps are not suitable?
Experienced city farmers do not recommend using conventional incandescent lamps. Firstly, they do not provide any benefit in growing plants. Secondly, they emit too much heat, which can damage crops and burn leaves.
Medical devices, lighting equipment for solariums and quartz lamps are not suitable as phytolamps for plants. Not only will they not bring results, they can lead to the death of all plants.
If the packaging does not describe the radiation spectrum or the phytolamp does not have red and blue spectra, then you should also refuse to purchase. There will be no benefit from such an acquisition.