Illumination is one of the most important criteria for choosing a location when placing a pot with an indoor flower or planting a seedling in open ground. Its intensity varies depending on the season of the year. For some plant species the need for it is higher, for others it is lower. Typically, the lack of natural sunlight is felt by plants in winter, as well as in December and March. If necessary, for light-loving species it can be compensated by turning on fluorescent or LED lamps.
Effect of light on plants
Light is the main source of energy necessary for the formation of hydrocarbons, fats and proteins that make up plant cells. It is absorbed by the green pigment of leaves, chlorophyll, and participates in the formation of organic substances along with water, carbon dioxide and trace elements. The combination of intensity and duration of solar insolation under natural conditions determines the change in phases of plant life - active growth, development of shoots and leaves, formation of buds, flowering, dormancy.
It is difficult for indoor plants to provide the required level of illumination for the following reasons:
- Light penetrates through a limited surface of window glass, so its intensity drops sharply at a distance from the windows.
- Window sills are often exposed to diffuse rather than direct sunlight.
- Windows on the lower floors of buildings are often obscured by nearby structures and trees.
- In rooms with dark wall surfaces and furniture colors, a significant amount of rays are absorbed by furnishings.
- When windows face north, northeast and northwest, less sunlight enters the rooms compared to south, east and west.
The upper floors of buildings and southern windows experience higher solar insolation, so flowers standing on window sills in the summer can get leaf burns and overheat.
To protect them from excess light, it is recommended to use shading of glass (sheets of paper, cloth) or place plants on shelves at some distance from the window.
It is better to place succulents on southern windows in summer. To protect the roots from overheating, you can place the pots in additional containers with sand or fine expanded clay.
How does changing the direction of light affect
Some flowers react to changes in the position of the bush in relation to the light source by dropping buds and flowers, for example, geranium, gardenia, fuchsia, and zygocactus. During the flowering period, it is not advisable to move them from place to place. In many species, shoots on the side of the light source grow denser and longer. For uniform development of decorative leafy plants, it is recommended to periodically rotate them along their axis by several degrees.
Effect of day length on flowering
The length of daylight hours has a significant impact on the flowering and fruiting of many crops. In a temperate climate zone, its shortest duration is 8 hours, maximum – 16 hours.
Based on the ratio of daylight hours and the onset of flowering, they are divided into:
- Species that require lighting for significant periods of time during the day. These include Saintpaulia, hydrangea, cineraria, gloxinia, calceolaria and some other flowers. Given sufficient daylight and good conditions, they grow and develop throughout the year. If these plants receive only natural light, they form and open buds from early spring to late summer.
- Species that bloom during short daylight hours (8 to 10 hours). These are plants such as zygocactus, poinsettia, chrysanthemum, azalea, and Kalanchoe Blossfeld.
- Indoor flowers that form buds at any length of daylight. These include evergreen begonia, rose, abutilon and some others.
- Plants that bloom when long daylight hours are replaced by short ones or vice versa. Thus, cyclamen and camellia bloom in winter, and grandiflora pelargonium blooms in spring.
What does a plant need in additional lighting?
In winter and early spring, throughout the fall, home mini-gardens and greenhouses need additional light from herbal devices. Be sure to illuminate indoor plants, seedlings for early harvests, as well as home herbs (basil, parsley, dill, rosemary).
In the rooms, the illumination level is 5000 lux, which is two times less than the norm required by plants (optimal 8-12 thousand).
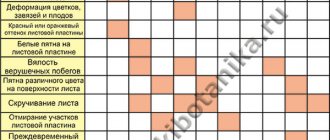
Signs of light deficiency:
- reduction in size and color saturation of foliage;
- stretching of internodes;
- stopping the formation of new buds.
Lighting is carried out according to schedule. You should adhere to biorhythms, use lamps with blue-violet and orange-red spectra.
Signs of too little or too much light
The ability of indoor flowers to adapt to light levels varies. There are light-loving, shade-tolerant and light-indifferent plants. Insufficient lighting has an adverse effect on plant development. Sensitivity to a decrease in its intensity is higher in light-loving species.
The lack of light is indicated by the following changes in the appearance and development of indoor flowers:
- Plants with light or variegated leaves change color due to an increase in the amount of chlorophyll to better absorb incoming light. They acquire a dark green color, sometimes become narrower and slightly elongated.
- The stems stretch in the direction of the light, but grow thin and weak. The length of the internodes increases, and at the same time their fragility increases.
- After some time, the growth of shoots and leaves stops due to deterioration of photosynthesis and lack of organic matter.
- Some plant species do not bud or bloom for a long time.
With excess light, the following changes are noticeable in the appearance of the bushes:
- The leaves turn yellow-green due to the partial destruction of chlorophyll. They can also lose turgor, drooping down, and in some cases dry out due to loss of moisture. When burned by the bright rays of the sun, the leaf plates acquire a bronze tint.
- The growth rate of stems decreases, the distance between nodes decreases, the width increases and the length of leaves decreases.
Making LED lighting for flowers with your own hands
There is no point in making LED lamps for a base. It's not practical. We will use LED strip. Making a homemade phytolamp for flowers comes down to three points:
- Calculate the required power of LED lighting for flowers.
- Select the tape model.
- Select a power supply.
LED lighting power calculation
The required illumination for the full growth of flowers is 10000-15000 Lux. Based on these figures, you should start when calculating LED lighting for plants.
Let's look at a specific example . We illuminate the seedlings in a box measuring 0.75 x 0.3 meters. We will provide plants with lighting of 15,000 Lux.
15,000 Lux – radiation intensity of 15,000 Lumens illuminating a surface of 1 m2 from a height of 1 meter.
Our illuminated area:
0.75m * 0.3m = 0.225 m2
So our required light intensity is:
15000 Lm/m2 * 0.225m2 = 3375 Lumens
Let's determine the height of the lighting. The resulting lighting intensity of 3375 Lm is needed when LED lamps for plants are located at a height of 1 m. By reducing the height by half, the required intensity will drop by a factor of 4 (inverse square law). By placing the lighting at a height of 0.5 m, we obtain the light intensity:
Inverse square law - when the distance to the light source increases by 2 times, the intensity of light radiation decreases by 4 times.
3375 / 4 = 845 Lm
All that remains is to select the LED strip according to these parameters.
Selecting LED strip to illuminate flowers
From the calculation, we obtained the required light intensity of 845 Lm. Given the size of the box with flowers, it is better to take 2-4 pieces of tape, 0.75 m long, to evenly cover the entire area.
The luminous flux of the LED strip is indicated per 1 m. If we only need 0.75m, then we need to add 25% to the luminous flux intensity declared by the manufacturer.
845 / 2 * 1.25 (we compensate for the length of the tape) = 530 Lumens (for two segments)
845 / 4 * 1.25 = 265 Lumens (for four segments)
Final parameters of the tape:
- Light intensity (brightness) 465 lm;
- Light temperature – combine warm + cold (3000K + 6000K);
- Supply voltage 12V is the most common type of tape.
SMD3528-W-60led is suitable for us - 3 meters, or SMD2835-W-60led - 1.5 m. Here you can read about tape markings.
Choosing a power supply for LED strips
It is important to choose a suitable driver for powering the lighting of indoor plants. There are only a few criteria:
- Power (most important);
- type of shell;
- additional functionality.
Power supply power calculation
. Let's look at the example of 3 meters of SMD 3528 tape, 60 LEDs per 1 linear meter. Power 1 l.m. 4.8W. Let's add 25% reserve for losses in connections and conductors and we get:
3m (length) * 4.8W (power 1 meter) * 1.25 (stock) = 18W.
Any power supply with a power of more than 20W and a voltage of 12V will do.
Type of shell . There are cases with different levels of dust and moisture protection, in an aluminum or plastic case with forced or natural cooling.
- We select the degree of protection depending on the operating conditions. At high humidity (placed inside greenhouses), the degree of protection should be at least IP67.
- Choose any body material. Doesn't provide any benefits.
- Forced cooling is necessary when the power supply is high (over 200W). Otherwise, passive cooling is sufficient.
Additional functionality . Power supplies can have remote control from a remote control, be equipped with LCD screens, and have timers. Purchase additional functionality as desired. The more functions, the more expensive the power supply.
Connecting the tape to the power supply
Connect all pieces of ice tape in parallel to the power supply. When connecting, use connectors (read more about connecting pieces of tape). One continuous section of tape should not exceed 5m in length.
Remember about the protection class of the LED strip for plants and the power supply. When choosing an IP20 class, place lighting and power in dry, dust-free places. If the class is IP67.68, you can even place it in wet greenhouses.
How much light do indoor plants need?
Recommended by topic
TOP 25 Most unpretentious indoor plants How to revive a home flower: drying, frozen, flooded at home 23 Houseplants that purify the indoor air
The need for light intensity differs between light-loving and shade-tolerant species. If the first grow better on eastern, western and southern window sills, the second group can also feel comfortable on a northern or partially obscured window by a tree or a neighboring house. In summer, it is advisable to shade windows facing south at midday, even for light-loving indoor flowers. Shade-tolerant plants are suitable for placement at a distance of up to 3 m from the window opening.
Light intensity is measured in lux. To determine it, a special device is used - a lux meter. On a summer day, the illumination of an east-facing window sill is approximately 2500 lux; a few meters away it drops to 500 lux. On normal winter days, the light intensity of the same window fluctuates between 500–1000 lux. If you move a little further from it, its performance decreases to values that are unable to provide even shade-loving species with sufficient light.
To compensate for the lack of natural solar radiation, artificial illumination with lamps is used.
When choosing the type of lamps, determining their optimal quantity and the distance at which it is best to place them from plants, their need for lighting depending on the time of year and day, the quality and spectral composition of the rays are taken into account.
It was experimentally discovered that at a light intensity of less than 300 and more than 3000 lux (for some of the most hardy species, above 10,000 lux), the development of flower bushes stops. Regarding the spectral component, observations have shown that the energy used in photosynthesis is absorbed from rays in the red range with a wavelength of 720 to 600 nm and orange in the range of 620–595 nm.
Also of great importance is the blue and violet spectrum of rays, necessary for the formation of protein molecules and the active growth of shoots and leaves. Their length is 490–380 nm.
Ultraviolet rays bring certain benefits. At wavelengths between 315 and 380 nm they prevent stem stretching and promote the production of a number of vitamins; at wavelengths between 280 and 315 nm they improve resistance to low temperatures.
Decorative lighting and lighting for plant growth
A lamp for growing indoor plants is a great way to extend daylight hours. After all, many indoor flowers are of tropical origin, which means they experience a daily lack of solar energy, especially in winter. For effective plant growth, the daylight hours should be about 15 hours. Otherwise, they weaken, stop blooming and are susceptible to various diseases.
When planning the future illumination of indoor flowers, it is important not to miss the aesthetic component. The phytolight should become part of the interior, a unique decorative element. There are a huge number of lamps on sale with wall mounts of different shapes, suitable for any energy-saving lamp: CFL or LED. Depending on the size of the home flower garden, lighting can be made from several spot lights aimed directly at each green pet, or from tubular fluorescent lamps with a reflector. Using your own imagination, you can make an original LED phytolight yourself.
How to choose a lamp
When choosing a lamp for supplementary illumination of plants, the preferences of individual species and varieties and the stage of development are taken into account. For example, for growing seedlings it is better to use LED lamps with a red and blue spectrum of rays. This will ensure uniform seed germination, proper development of seedlings, and the formation of healthy shoots and leaves. In principle, the versatility of LED lamps allows them to be used for any type of indoor and greenhouse plants. You just need to adjust the color and intensity of the lighting in each specific case.
For a free-standing bush or a small container with seedlings, it is enough to use a lamp with an E27 base, which is designed to be screwed into regular sockets.
A linear lamp will provide light to the entire surface of a window sill or flower stand. Large light panels are suitable for installation in a greenhouse or winter garden, covering a significant part of the space.
Fluorescent fluorescent lamps are suitable for additional illumination of plants in winter and during the dormant period. Sodium lamps with red radiation ensure abundant flowering and fruiting of greenhouse crops. For example, they will allow tulips to bloom almost simultaneously by March 8th. The absence of the blue spectrum in the glow of sodium lamps stimulates the high growth of stems of roses grown for cutting.
Guseva Ulyana
Ask a Question
Question to the expert
How to calculate the required power of a phytolamp to illuminate 1 m2 of area?
For plants located on or near a windowsill, 40 W per 1 m2 is sufficient. For the most light-loving species and when grown at a considerable distance from the window, a lamp with a power of 60 W is required to illuminate the same amount of area.
Calculation of the power of fluorescent lamps and some more numbers
There are three main types of plants, due to which there are differences in the strength of plant illumination: shade-tolerant, loving moderate lighting, light-loving. For them, you need to select artificial lighting for plants accordingly - 0.5–1.5, 1.5–2.5, more than 2.5 watts for a green area equal to 10 × 10 cm, or 1 sq. dm.
As already mentioned in the article, the properties of such lamps have been sufficiently studied so that calculations can be carried out using specific figures for average lamps. For each case specifically, you will need to use the existing parameters and conditions. This calculation will present the theoretical power of the light bulbs and the area of greenery that needs to be illuminated.
Let the flower rack have an area of 150 square meters. dm. There are flowers on the rack that love moderate lighting, so let’s take the middle in the above interval - 1 W. Thus:
150 sq. dm. × 1 W = 150 W
It turns out that in order to illuminate the selected rack of a fairly impressive size of 1.5 square meters. m, you need a lamp with light bulbs with a total power of 150 W.
By placing the bulbs at a height of 15–25 cm, we will get the best lighting effect.
Correct lamp installation
When placing the lamp, it is necessary to take into account that the light intensity decreases in proportion to the distance from the plant: if the distance from the top point of the bush is increased by 2 times, its illumination will decrease by 4 times. To prevent the rays from scattering to the sides, the lamps are equipped with reflectors. It is advisable that the surface of the walls is also light or covered with foil (for example, in a greenhouse) to reduce light loss.
It is recommended to place the phytolamp as close as possible to the plant, but not less than 10–15 cm from it. These numbers are relevant when growing seedlings.
For bushes of medium height, the lamps are placed 20–30 cm above their surface. When the lamp is removed more than 50 cm, its effectiveness decreases significantly. As plant growth gradually increases, it becomes necessary to raise the lighting fixture higher from time to time. Also, the distance between the flower and the lamp is adjusted based on the power of the lamp and the needs of the species being grown.
Advantages and disadvantages of use
The main advantage of fluorescent lamps is that they do not produce hot light, so flowers do not get burned. There are other advantages:
- duration of service life;
- high color rendering rates;
- efficiency;
- optimal spectrum for plant growth;
- affordable prices.
Flaws:
- difficulty in connecting;
- when they fail, they require special disposal;
- high cost of quality models;
- there are harmful substances inside the lamp;
- Over time, the quality of light transmission decreases.
Rules for handling when a lamp fails.
How to tell if your plants are getting enough light
Recommended by topic
Delphinium Carnation Catharanthus
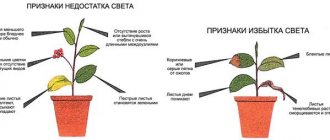
The lack of lighting can be inferred from the appearance of the bushes. To better use all incoming rays, the surface of the leaves turns in the direction of the light source. Increased production of chlorophyll begins in the cells, due to which light-colored or variegated leaf blades acquire a rich dark green hue. New leaves at the top of the stem are pale and slightly colored.
The shoots lengthen, trying to be closer to the light. At the same time, they become thin and brittle, with unnaturally elongated internodes. The lower leaves, which are most acutely experiencing a lack of light, begin to turn yellow and gradually fall off, because of this the base of the stem is exposed. The plant stops forming buds, flowers appear less frequently, are small and faded, or flowering is completely absent.
How to add light to plants? Plant lamps
When choosing a lighting device, you should take into account not only the intensity, but also the spectrum of light radiation. It is known that plants do not absorb all rays, but only those in the blue and red spectrum. Orange-red and blue-violet rays are optimal. Orange-red light promotes seed germination and shoot growth, while blue-violet light stimulates the development of green mass.
IN THE PHOTO: Plants and people “see” light differently. The human eye distinguishes yellow-green shades in sunlight and does not see blue and red at all. Plants, on the contrary, are sensitive to the blue and red regions of the spectrum and to a lesser extent to the yellow-green
Fluorescent, gas-discharge, LED, and incandescent lamps are used as artificial lighting sources. In this review article we will recommend the simplest and most affordable options: special phytolamps of the T8 type (regular tubular) Osram Fluora or its analogue Sylvania GroLux. Despite the low power (the maximum of these lamps is 58 watts with a length of more than 1.2 m), they provide excellent illumination even for tropical plants. In particular, Gardenia blooms profusely in winter under the pink light of these lamps. If it is not possible to purchase them, we recommend the brightest fluorescent lamps from Philips or Osram. They are often T5 type - these are thinner tubular lamps for compact luminaires. They shine better than regular T8s.
Ask sellers to show you lamps with a color temperature of 5500–6500 Kelvin. Usually on packaging this color temperature corresponds to the phrase white ”. Fluorescent lamps labeled Warm white (“warm white”) have more orange-red rays in their spectrum, which are also important for plants. Ideally, you combine one “cool white” light and one “warm white” light in one lamp.
But it is better not to use ordinary incandescent light bulbs with a tungsten filament for additional illumination. The light intensity of such devices is low, but at the same time they produce such an amount of heat that they simply burn the plants.
IN THE PHOTO: Phytolamp for additional illumination of plants Osram Fluora - a good alternative to natural lighting
Reflectors or reflectors play an important role in illuminating plants. Thanks to the reflective surface, they collect scattered light and direct it back to the plant, which greatly increases the efficiency of the lamps. Many modern lighting fixtures have built-in reflectors, but you can buy them separately or make them yourself from scrap materials. Metallized and white matte surfaces, for example, food foil (but not the glossy, but the matte side), white fabric or white opaque polyethylene reflect the rays best. But an ordinary mirror reflects only 40% of the rays needed by the plant, so it is better not to use ordinary mirrors.
What light is best for growth?
The growth of shoots and the appearance of new leaves occurs normally in the red and blue spectrum of radiation. Active photosynthesis requires light wavelengths from 300 to 720 nm. The blue spectrum promotes the formation of proteins and carbons. Ultraviolet rays prevent the elongation of stems and increase the synthesis of vitamins. The red and orange spectrum improves flowering and fruiting, and seed germination.
Options for placing lighting for seedlings
- Individual illumination of plants with LEDs.
- Racks for plants.
Individual plant lighting.
Spot lighting of plants will not only avoid the annual relocation of all pots and flowerpots to the wintering place, but also create a unique, inimitable interior design. Miniature but powerful LEDs can be used as a lighting source.
LEDs for illuminating plants are capable of producing up to 120 lumens and can be used both as illumination for a plant and as a night light.
For individual lighting, you can buy a specialized LED phytolamp, which we wrote about above. The calculation method is the same as for the LED strip.
Racks for plants.
If there are a large number of lighting objects, it is more advisable to make shelves at the bottom of which the LED strip for plants will be mounted.
Racks can be protected with reflective materials: foil, metallized insulation. This will provide round-the-clock illumination, but will not interfere with rest in the evening. Also, such a screen will increase the illumination of plants by 10-15 percent.
Lighting in winter
In the winter months, flowers should be moved to the brightest window sills, moved from the north side of the house to the southern and eastern windows.
For the most light-loving species, it is advisable to provide additional lighting.
For these purposes, LED lamps are used. They are economical and provide the entire required radiation spectrum. Minimal heat generation allows these lamps to be placed at a short distance from the plant.
Also, for illuminating seedlings and light-loving species of compact size, energy-saving lamps Foton, Elektrox, TNeon fluorescent lamps are suitable, for bushes in the flowering and fruiting stages - sodium HPS Grolux, Green Power, Prima Klima, etc. For effective operation of these devices, reflectors and ballasts should be used devices.
Question to the expert
Please tell me how many hours a day should indoor plants be illuminated?
It is desirable that the total duration of illumination be 12–14 hours. For example, with an 8-hour daylight hours, the flowers are illuminated for 4–5 hours. If the intensity of solar radiation is insufficient in cloudy weather, in a north-facing or shaded window you can turn on the lamp during the day. When germinating seeds, when the entrances appear, the light can not be turned off for the first 3 days, then gradually over several days the duration of additional lighting is increased to 14 hours.
What should you consider when installing such lighting?
How to choose the best conditions? The following will be a list of recommendations that it is advisable to follow when installing lamps to achieve maximum efficiency of artificial lighting.
- A very important issue is the level of the lamps above the plants. Below in the article we will give an example of calculating the required amount of light for given parameters, but now there are a few theoretical nuances.
- The closer the lamp is to the surface of the leaves (for plants) or to the soil (for low seedlings), the greater the effect of the installed light for illuminating plants in lux.
- It should be borne in mind that an excess of glow can also have a detrimental effect on the health of flowers - they can begin to turn yellow and wither, gradually restoring their condition when the light is turned off.
- Although the lamps give off a little heat, it is still present. Their close location can quickly evaporate moisture from the soil surface, which is very harmful to ascending seedlings. Remember to control the soil moisture and raise the lamp slightly.
- Initially, mount the lamps so that you can change the height of the lamp to illuminate the plants. If there is no improvement, move closer. If the leaves initially recovered, but began to wilt again, move them away. Gradually you will achieve the optimal location.
Lighting arrangement for climbing seedlings
- If plants are fully supplied with artificial light, it is important to observe the duration of the lighting. Here's what to consider:
- If completely artificial lighting is used, try to observe daylight hours to maintain the natural biological rhythms of flowers. Turn on the lights, for example, at 8 am, and turn them off at 9–10 pm. 13–14 hours of properly adjusted light will be enough, you can even reduce it to 11–12 if this does not affect the condition of the plants.
- When using partial lighting for indoor plants (in addition to natural light), it should be turned on during the period of the day when natural light begins to fade. Usually you need to supplement about 5 hours of daylight. Rarely more.
- For seedlings the story is different. For proper growth, the ground must be illuminated around the clock. When they become strong enough, daylight hours for them are reduced to 14–16 hours.
Also take into account the difference in weather; in cloudy weather it is necessary to turn on the lamps for a longer time.
If you have a hard time keeping track of time (or just to ensure consistency), you can use electronic or mechanical timers. They will create a stable daylight hours, eliminating routine monitoring of the clock hands.
Houseplants that require a lot of light
The most light-loving species include myrtle, pineapple, roses, Kalanchoe, spurge, citrus fruits, bocarneya, bougainvillea, southern cordyline, hibiscus, pittosporum, succulents, yucca, acacia, oleander. They require high lighting intensity - from 4000 lux.
At a short distance (up to 2 m) from a sunny window, avocado, banana, gardenia, hibiscus, lily, ficus, coconut, coffee tree, begonia, zamioculcas, dracaena, passionflower, cyclamen, primrose, caladium, gloxinia, sundew, zantedeschia feel comfortable , saintpaulia, gardenia, araucaria, cyperus, abutilone.
East windows
There is much less illumination on the eastern windows than on the southern ones, and they differ from the western ones in that in the morning the rays are not so scorching and shading on the eastern windows is not required. Plants of the eastern window include: asparagus, aucuba, tree begonia, hairy begonia, metallic begonia, emerald begonia, griselinia, dracaena angustifolia, dracaena deremenskaya, butcher's broom, myrtle, ivies, cissus, pittosporum, fatsia japonica, violet uzumbara, ficus, Roussel's epiphyllum , epiphyllum obtuse.
Indoor plants that don't require a lot of light
From 1000 to 3000 lux of light is sufficient for ferns, gesneria, bromeliad, billbergia, fittonia, scindapsus, shieldweed, davallia, aspidistra, fatsia, ivy (without variegated leaf color), bellflower, Venus flytrap, dwarf ficus, pellea.
Diffused light with an intensity of 3000 to 4000 lux is needed for aglaonema, tillandsia, fuchsia, begonia, nepenthes, variegated ivy, streptocarpus, mimosa, clivia, cirpus, asparagus, tradescantia, balsam, philodendron, syngonium, tillandsia, clusia, rhododendron, antur iyumu.
The correct placement of plants on windows or at some distance from them contributes to a beautiful appearance and active development of bushes. During the dormant period, indoor flowers should be provided with sufficient lighting, slightly reducing the air temperature in the room. Various types of lamps with red and blue wavelengths are suitable for additional lighting. Additional lighting of seedlings will allow you to obtain strong and well-developed seedlings.
Which window should you place your favorite flower on?
East side
On the east side, soft light for indoor plants occurs only in the morning. It is favorable for the following colors:
- Asparagus, azalea
- Begonia, gardenia
- Dieffenbachia, dracaena
- Clerodendrum, calathea, crossandra
- Arrowroot, nepenthes, nephrolepis
- Roicissus and poinsettia
- Certain types of ficus, philodendron
- Chovea, Eschynanthus and Aechmea
In the southern regions, these flowers are placed in the northeast, in the northern regions – in the southeast.
Asparagus
South side
The windows of the southern rooms are filled with the maximum amount of light. In the northern regions, this is the best place for flowers.
- Abutilone, brugmansia
- Gloriosa, hibiscus
- Indoor rose and jasmine
- Catharanthus, cacti
- Pachystachys, passionflower
- Setcreasia, succulents
- Thunbergia, ficus benjamina, date
- Hoya, chlorophytum, yucca
On hot days, flowers on a south window should be ventilated and periodically sprayed to compensate for dry air.
Abutilone
West side
The windows on the west side are illuminated by the sun at sunset. The arrangement of flowers here is especially appropriate for summer days in the southern regions.
A room facing west maintains a constant daily temperature, which is beneficial for flower growth.
Suitable for Western rooms:
- Akalifa, Allamanda
- Brunfelsia and Vriesia, Guzmania
- Dendrobium and jacaranda
- Cattleya, godson
- Monstera and Pisonia
- Saintpaulia, stephanotis
- Fuchsia, cyperus
Akalifa
North side
The northern windows receive little light and remain in shadow throughout the day. Plants in rooms are installed no further than 2 m from the window.
Flowers for northern shade:
- Crescent asparagus, adiantum, unturium, aspidistra
- Blechium, davallia, fragrant dracaena
- Bluebell, clivia, ivy
- Scindapsus, selaginella
- Fittonia, ficus dwarf
- Cissus, cirtomium
Maidenhair