Every experienced gardener knows the huge role that properly selected lighting for indoor plants plays. Along with watering and soil, light is an indispensable component on which successful growth directly depends. It is no secret that in the natural environment, some plants thrive in shaded areas, while others cannot develop without direct exposure to sunlight. At home, the situation looks similar. Let's talk in detail about how to properly make artificial lighting for indoor plants.
Decorative lighting and lighting for plant growth
A lamp for growing indoor plants is a great way to extend daylight hours. After all, many indoor flowers are of tropical origin, which means they experience a daily lack of solar energy, especially in winter. For effective plant growth, the daylight hours should be about 15 hours. Otherwise, they weaken, stop blooming and are susceptible to various diseases.
When planning the future illumination of indoor flowers, it is important not to miss the aesthetic component. The phytolight should become part of the interior, a unique decorative element. There are a huge number of lamps on sale with wall mounts of different shapes, suitable for any energy-saving lamp: CFL or LED. Depending on the size of the home flower garden, lighting can be made from several spot lights aimed directly at each green pet, or from tubular fluorescent lamps with a reflector. Using your own imagination, you can make an original LED phytolight yourself.
Making LED lighting for flowers with your own hands
There is no point in making LED lamps for a base. It's not practical. We will use LED strip. Making a homemade phytolamp for flowers comes down to three points:
- Calculate the required power of LED lighting for flowers.
- Select the tape model.
- Select a power supply.
LED lighting power calculation
The required illumination for the full growth of flowers is 10000-15000 Lux. Based on these figures, you should start when calculating LED lighting for plants.
Let's look at a specific example. We illuminate the seedlings in a box measuring 0.75 x 0.3 meters. We will provide plants with lighting of 15,000 Lux.
Our illuminated area:
0.75m * 0.3m = 0.225 m2
So our required light intensity is:
15000 Lm/m2 * 0.225m2 = 3375 Lumens
Let's determine the height of the lighting. The resulting lighting intensity of 3375 Lm is needed when LED lamps for plants are located at a height of 1 m. By reducing the height by half, the required intensity will drop by a factor of 4 (inverse square law). By placing the lighting at a height of 0.5 m, we obtain the light intensity:
3375 / 4 = 845 Lm
All that remains is to select the LED strip according to these parameters.
Selecting LED strip to illuminate flowers
From the calculation, we obtained the required light intensity of 845 Lm. Given the size of the box with flowers, it is better to take 2-4 pieces of tape, 0.75 m long, to evenly cover the entire area.
The luminous flux of the LED strip is indicated per 1 m. If we only need 0.75m, then we need to add 25% to the luminous flux intensity declared by the manufacturer.
845 / 2 * 1.25 (we compensate for the length of the tape) = 530 Lumens (for two segments)
845 / 4 * 1.25 = 265 Lumens (for four segments)
Final parameters of the tape:
- Light intensity (brightness) 465 lm;
- Light temperature – combine warm + cold (3000K + 6000K);
- Supply voltage 12V is the most common type of tape.
SMD3528-W-60led is suitable for us - 3 meters, or SMD2835-W-60led - 1.5 m. Here you can read about tape markings.
Choosing a power supply for LED strips
It is important to choose a suitable driver for powering the lighting of indoor plants. There are only a few criteria:
- Power (most important);
- type of shell;
- additional functionality.
Power supply power calculation
. Let's look at the example of 3 meters of SMD 3528 tape, 60 LEDs per 1 linear meter. Power 1 l.m. 4.8W. Let's add 25% reserve for losses in connections and conductors and we get:
3m (length) * 4.8W (power 1 meter) * 1.25 (stock) = 18W.
Any power supply with a power of more than 20W and a voltage of 12V will do.
Type of shell. There are cases with different levels of dust and moisture protection, in an aluminum or plastic case with forced or natural cooling.
- We select the degree of protection depending on the operating conditions. At high humidity (placed inside greenhouses), the degree of protection should be at least IP67.
- Choose any body material. Doesn't provide any benefits.
- Forced cooling is necessary when the power supply is high (over 200W). Otherwise, passive cooling is sufficient.
Additional functionality. Power supplies can have remote control from a remote control, be equipped with LCD screens, and have timers. Purchase additional functionality as desired. The more functions, the more expensive the power supply.
Connecting the tape to the power supply
Connection diagram to the power supply
Connect all pieces of ice tape in parallel to the power supply. When connecting, use connectors (read more about connecting pieces of tape). One continuous section of tape should not exceed 5m in length.
Remember about the protection class of the LED strip for plants and the power supply. When choosing an IP20 class, place lighting and power in dry, dust-free places. If the class is IP67.68, you can even place it in wet greenhouses.
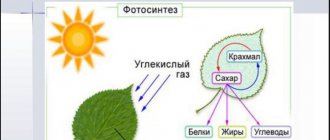
The most important component of growth is the light spectrum
In order to understand how inhomogeneous light is from different electrical sources and the sun, you need to look at their spectral composition. The spectral characteristic is the dependence of the radiation intensity on the wavelength. The solar radiation curve is continuous throughout the visible range with a decrease in the UV and IR regions. The spectrum of artificial light sources in most cases is represented by individual pulses of different amplitudes, which as a result gives the light a certain hue.
During the experiments, it was found that for successful development, plants do not use the full spectrum, but only its individual parts. The following wavelengths are considered the most vital:
- 640–660 nm – velvety red color, necessary for all adult plants for reproductive development, as well as for strengthening the root system;
- 595–610 nm – orange for flowering and fruit ripening;
- 440–445 nm – violet color for vegetative development;
- 380–400 nm – near UV range to regulate the rate of growth and formation of proteins;
- 280–315 nm – mid-UV range to increase frost resistance.
Lighting with only the listed rays is not suitable for all plants. Each representative of the flora is unique in its “wave” preferences. This means that it is impossible to fully replace the sun's energy using lamps. But artificial lighting of plants in the morning and evening hours can significantly improve their life.
How to use at home?
The lamp body, also known as the radiator, must be in contact with air for better cooling. Therefore, do not use lampshades, or install an electric fan to cool the case.
Place lamps above the plants so that the light falls down, similar to sunlight. The first days after germination, the installation should operate around the clock. If properly cooled, this will not cause any malfunctions.
When choosing full spectrum lamps that completely replace sunlight, be aware of the damage they can cause to your eyes. To avoid this, install such lamps in non-residential premises or choose more expensive models that provide compensation for harmful effects.
Signs of lack of light
There are a number of signs by which it is easy to identify a lack of light. You just need to take a close look at your flower and compare it with the standard. For example, find a similar view on the Internet. A clear lack of illumination manifests itself as follows. The plant slows down its growth. The new leaves are smaller and the stem becomes thinner. The lower leaves turn yellow. The flower either stops blooming completely, or the number of buds formed is less than the statistical average. It is assumed that watering, humidity and air temperature are normal.
How much light do you need?
It is impossible to give a definite answer to this question. Just as a person can live in different parts of the globe, so an indoor flower can grow on a windowsill facing north, south, west or east. Throughout its life, the plant will strive to adapt to current conditions: stretch upward due to lack of light or, conversely, expose the next blossoming bud to the sun’s rays.
By observing the appearance of the stems and leaves, the size and number of flowers, you can determine the adequacy of the lighting level. At the same time, do not forget about what stage of development the indoor flower is at: growing season, flowering, seed ripening. At each stage, it takes light from the sun of the wavelength that it needs at the moment. Therefore, when organizing additional lighting, it is important to take into account the qualitative component of the light flux.
Long-term exposure to bright light from the sun and lamps with an illumination level of more than 15 thousand lux is favored by those indoor flowers that grow in the open air in their natural habitat. These are many people's favorite crassula, geranium, kalanchoe, and begonia. Artificial lighting for plants of this type in the evening will benefit them.
Representatives of the flora that feel comfortable in illumination of 10–15 thousand lux include spathiphyllum, clivia, saintpaulia, tradescantia and dracaena. The leaves of these types of indoor flowers do not like hot sunlight, but also do not tolerate early twilight. Therefore, the ideal place for them would be a window sill with access to the west, where in the evening their leaves will receive the necessary energy from the setting sun.
So-called shade-loving plants can bloom and develop away from the window opening, being content with illumination of up to 10 thousand lux. However, this does not mean that they will die if they are placed in a brighter place. They just need less direct sunlight. These include some types of ficus and dracaena, philodendron, as well as tropical vines.
Supplementary lighting for plants and artificial lighting sources
In most cases, indoor plants need additional lighting. Flowers, which at first glance have bright green succulent leaves and bloom regularly, will look even better if they are exposed to a phytolamp. If someone thinks otherwise, then he has an excellent chance to be convinced of the error of his thinking and assemble a phyto-lamp with his own hands. To extend daylight hours, various sources of artificial light are used. Let's look at each of them and figure out which light is best for plants.
Incandescent lamps
Illuminating plants with incandescent lamps is the least effective for several reasons. The emission spectrum of conventional light bulbs with a spiral is strongly red-shifted, which does not contribute to photosynthesis in any way. Low efficiency and, as a consequence, enormous heat generation drive their energy and light efficiency to zero. In addition, incandescent lamps have the shortest service life compared to other artificial light sources.
Fluorescent lamps
Tubular fluorescent or, as they are most often called, energy-saving fluorescent lamps of the T8 full spectrum type (T = 5300–6500°K) are considered the best option for illuminating indoor plants for many years.
They have earned many positive reviews due to the presence of a selective spectrum, efficiency and low heat transfer combined with reasonable cost. Companies specializing in the production of fluorescent lamps offer plant growers an improved option - a phytolamp with a selective emission spectrum. They work predominantly in the blue and red range, as can be seen from the characteristic glow. But the cost of such lamps for illuminating plants is an order of magnitude higher than their conventional counterparts.
DNAT
A sodium lamp is the most efficient light source. In terms of luminous efficiency and working life, these lamps are comparable to LEDs for plants. But they are not suitable for home use due to their excessively high brightness (more than 15 thousand lux). But in many greenhouses and conservatories, growing plants under artificial lighting is based precisely on gas-discharge lamps. Due to the fact that they emit more red light, they are installed in combination with 6500K fluorescent lamps.
LED light sources
All LED phytolights are divided into three groups:
- bicolor;
- with multispectrum;
- with full spectrum.
Bicolor or two-color lamps are based on blue (440–450 nm) and red (640–660 nm) LEDs. Their light is considered to be the most optimal for organizing illumination of any plants during the growing season. This working spectrum favors the process of photosynthesis, which leads to accelerated growth of green mass. That is why summer residents prefer blue-red LED lamps when growing vegetable seedlings on the windowsill.
LED lamps with a multispectrum have a wider application due to the expansion of the red range into the region of infrared and yellow light. They are in demand for illuminating adult plants, stimulating flowering and fruit ripening. In apartment conditions, it is better to use LED multispectrum for flowers with a dense crown.
A phytolight with a full spectrum of radiation can be used to illuminate flowers in an apartment, regardless of the type and location. This is a kind of universal artificial light source that emits over a wide range with maximums in the red and blue zones. The full spectrum LED lamp is a tandem of energy efficiency and light energy reminiscent of the action of sunlight.
Today, the creation of favorable conditions for a widespread transition to phyto-LEDs is not happening for two reasons:
- high cost of high-quality lamps for plants;
- a large number of fakes based on conventional LEDs.
Types of lamps
To provide normal additional lighting or to completely illuminate a houseplant in an apartment, several types of light bulbs are used. These are traditional incandescent lamps, halogen, LED lamps, lamps, LED strip. Let's consider their characteristics and features.
Incandescent lamp
This is the most common type, which everyone is familiar with - there are or were such lamps in every apartment. Due to electrical energy, the tungsten spiral, which is located in a glass container, is heated. The device is screwed into the socket, and no special equipment is required for connection.
The disadvantage is the fact that there is no blue color in the spectrum. The light output is very low and amounts to 17-25 Lm/W. This is not the best choice for indoor plant lighting. The lamp gets very hot and if placed above flowers even at a height of 1 m, it can cause burns. If you raise the lamp more than 1 meter, the lighting efficiency will tend to zero.
Luminescent
A fluorescent lamp is a bulb with electrodes on each side. They are connected by a tungsten helix. Inside the tube there are inert gases or mercury vapor. A special layer of phosphor is applied to the inner surface of the flask.
This is what a fluorescent lamp looks like
There are three types of such lamps:
- general purpose products;
- special purpose;
- compact models.
The general-purpose model has good characteristics - high light output, low heat emission, and long service life. In plant growing, they are used to organize additional illumination of indoor plants when the daylight hours are short. But the main thing about these lamps is their very limited spectrum. It is not recommended to use paws for constant lighting.
Special-purpose fluorescent lamps are distinguished by the presence of a phosphor layer. Due to this improvement, the spectrum of the lamp is very similar to that needed for plants. This lamp can be selected in cases where it is necessary to provide full illumination and periodic additional illumination. Also, these lamps are often chosen for creating decorative lighting with your own hands.
The disadvantages include the inflated cost and an electronic ballast installation, without which it will not be possible to connect the device to the network. The lamp can provide the right light, but it is recommended to use it only when there are no other devices with a power of 200-300 W.
Gas discharge
These products are capable of generating the brightest light. There are several types of these lamps; mercury, sodium, and metal halide can be distinguished. Mercury models are among the very first. There is no special coating on the inside of the bulb, and the light output coefficient is very low. They emit light with a bluish tint that is unpleasant both for the human eye and for green friends.
Updated models with improved spectral characteristics are now being produced. They have become one of the lighting options for greenhouses and greenhouses. But the problem with heat transfer has not yet been solved.
Sodium models have greater brightness; these are effective models with high light output and long service life. The spectrum is in the red zone. With two lamps you can illuminate a huge area in the winter garden or a large collection of plants. To ensure balance in the spectrum, it is recommended to alternate mercury and halogen models. Green plants will be happy.
Metal halide light bulbs are the most advanced devices for lighting home plants, as well as greenhouses and greenhouses. They differ in the following characteristics:
- high power;
- high service life;
- optimal spectral balance.
To use such light bulbs in your home, you will need to purchase a special socket. There is also one big drawback of such lamps - the cost. It is significantly higher than the price of basic analogues.
What light is best for growth?
Of course, the ideal light source is solar energy. In apartments with windows facing southeast and southwest, you can grow any flowers, placing them in different parts of the room. But don’t be upset for those who only have a north-facing view from their window. Fluorescent and LED lamps for lighting plants compensate for the lack of sun rays.
Fluorescent lamps for plants are a time-tested budget option. They are suitable for those who are trying to create normal conditions for a flower with little investment. LED phytolamps are for those who want to speed things up and achieve the best results in a short time, despite the price of several thousand rubles.
How to choose it?
The housing is of great importance for the correct operation of the lamp; it must dissipate heat. Choose lamps with an aluminum body that serves as a radiator.
Wattage is an important factor in determining the effectiveness of your lighting, but the number of watts you need in the lamps depends on the height at which you hang it and the area you need to illuminate.
The shape of the LED phytolamp can be easily adjusted to your needs.
- Need to light up your windowsill? It would be correct to use both an LED panel and a branch with several lamps.
- Do you have a vertical stand or a single plant? The option with a plinth is perfect.