Fertilizing garden flowers
If your flowers do not receive the required amount of nutrients, then you should not expect abundant and long-lasting flowering from them, and their appearance will leave much to be desired.
Humic fertilizers
promote rapid rooting of plants, their growth, flowering, increase immunity, improve nutrition, reduce nitrate content in the soil and prevent buds from falling off.
Apply humic fertilizers
in small quantities, because an overdose is dangerous and you will experience the exact opposite effect than you expected. Here it is good to apply the principle that less is more.
Humic fertilizers
obtained from sapropel, peat, oxidized brown coal. In general, humic fertilizer is a nitrogen-containing complex mixture of natural compounds.
For spring tillage, a week before planting flowers on the site, dissolve 3 caps of humate in a bucket of water and water the soil (3 liters of solution per 1 m²). Then cover the soil with a flat cutter and mulch.
Then fertilizing is carried out during the formation of buds on the plants: 1 cap of humate per bucket of water and irrigate the plants with the resulting solution.
Organic fertilizers stimulate the activity of soil microorganisms, such as worms and fungi, which improves soil quality and helps mineralize organic matter. Organic fertilizers, by stimulating the activity of microorganisms and improving the quality and condition of the soil, affect the air and water nutrition of plants.
Organic fertilizers include: manure, peat, green manure, bird droppings, ash, legumes.
Fresh cow dung
It cannot be applied as a fertilizer immediately, it must be passed through the compost, it must rot.
You can make liquid organic fertilizer from cow manure
. To do this, you need to take 1 kg of manure per bucket of water, let it sit for a day and then use it. But you can fertilize with horse manure right away.
To make organic fertilizer from chicken manure
Take 1 kg of chicken manure in a bucket of water and leave to infuse for two weeks. Then, to feed, use 1/2 liter of the resulting slurry per bucket of clean water.
Peat
It perfectly regulates soil moisture, and is also used as a loosening agent for heavy clay soils and as compost along with other types of organic fertilizers.
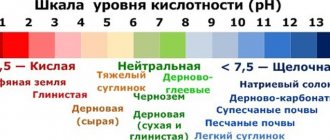
When adding peat, liming is necessary. With high soil acidity, pH5 and below, 1/2 limestone or chalk is added for every square meter of loamy and clayey soil. Add 0.3 kg of chalk or limestone to sandy soils.
Peat compost:
two months after deoxidation, add cow manure 1:3, mix, cover with straw on top and leave for 4 months. After the expiration date, use it as fertilizer.
Ash
used when planting in holes immediately when planting plants along with compost.
Green manure
Collect, chop, put in a large container, add water and leave to ferment for two weeks, stirring the solution daily. After two weeks, fermentation will end and the plants can be fertilized.
If you made liquid organic fertilizer from nettles
, then before applying it as fertilizer it should be diluted 1:10. Onions, peas and beans cannot be fed with this fertilizer!
Legumes
rich in nitrogen and their aboveground part is a wonderful green fertilizer. The green mass of legumes, after being incorporated into the soil, very quickly mineralizes and fertilizes the area with nitrogen. Lack of nitrogen leads to the fall of buds, the leaves turn yellow and die.
The following flowers do not like organic fertilizers:
tulips, hyacinths, daffodils, asters, nasturtium, marigolds.
The main mineral fertilizers for garden flowers are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Nitrogen
is responsible for the rich green color of the leaves and stems of the plant. With a lack of nitrogen, chlorosis appears: plant growth slows down. the leaves turn yellow and fall off, the buds die. With an excess of nitrogen, plants bloom poorly and grow very strongly.
Phosphorus
promotes plant growth and development. If there is an overabundance, the lower leaves wrinkle and die, and the plant decreases in size. With a lack of phosphorus, plants bloom later (if they bloom at all) and the leaves acquire brownish-purple spots.
Potassium
Helps resist fungal diseases and restores plant immunity. With a lack of potassium, the shape of the leaves is distorted and brown spots appear along the edges.
Author: Elena Grigorieva AlenKKKa
Copy the article only with an active link to the “Dachnitsa” website and indicate the author of the article.
How to use horse droppings for onions and garlic.
Since onion and garlic crops are very demanding of loose, fertile soil with a neutral reaction. Horse manure is practically irreplaceable when growing these crops on heavy clay soils.
As a rule, onions and garlic are planted mainly before winter and therefore spreading manure over the surface of the ridges in the autumn is not suitable for us. Therefore, horse droppings are applied under the onion and garlic beds in spring and summer.
Well, if you don’t have enough space in your garden to leave unsown plots empty. Then we add humus to the ridges immediately before planting winter garlic or onions. Based on a bucket of humus per square meter.
Reviews from gardeners
One-year-old manure is not yet completely rotted. For pumpkins - cucumbers, watermelons, zucchini, etc. even fresh manure will be a blessing. But for root vegetables I would not rush. As a last resort, I would not dig it up but lay it in the rows, like mulch. When manure gets into the soil (not rotted, then all chemical soil processes do not go correctly)
Sergius
https://otvet.mail.ru/question/166373265
Carrots and beets need poorer soil; do not overdo it with unripe humus (this is manure from last fall). The carrots will be horned and cracked, and the beets will be empty inside and with black spots. In general, root vegetables tend to accumulate nitrates from manure. This also applies to potatoes, they are better in humus. From manure it also grows huge and empty, rots during storage and turns black when cooked.
without GMO
https://otvet.mail.ru/question/166373265
Dry some of the manure, grind it and sprinkle the furrows with carrots... I do this every year... and I don’t regret it... and cucumbers, zucchini and pumpkin can be sown directly in the heap... the harvest will be excellent...
Prankster
https://otvet.mail.ru/question/166373265
Manure as a fertilizer is not suitable for all vegetable crops. Some flowers respond poorly to the application of manure, so before using it on a personal plot, it is worth analyzing what crops will be planted in the beds.
With your own hands
In addition to store-bought preparations and organics, experienced gardeners use fertilizing from improvised means. Such fertilizers are prepared independently and contain a maximum of vitamins.
- Baker's yeast. 40 g of yeast are infused in 1000 ml of warm water. This fertilizer should be applied in very strong dilution (optimal concentration - 1%). Thanks to the abundance of B-vitamins and cytokinins, perennials noticeably come to life and begin to grow.
- Wheat sourdough. Wheat grains are soaked for 24 hours, then a large spoonful of flour and sand are added. Bring to a creamy state, cook over low heat (with constant stirring) for 25 minutes. Next, cool, cover with gauze and leave in a warm place to sour. Once the infusion begins to bubble, the fertilizer is ready for use. Dosage – a tablespoon per 1000 ml of water. This fertilizing not only supplies vitamins, but also prevents the development of pathogenic microflora in the soil.
- Succinic acid. One tablet is diluted in 1000 ml of water. The solution is used for watering and simultaneous feeding. Being a powerful growth stimulator, succinic acid is capable of resuscitating severely depleted and dying perennials. Frequency of application – once every 5 years.
Features of manure fertilizers
In general, manure is a multiphase system consisting of solid, liquid and gaseous substances, and depending on the type of animal husbandry, it can be obtained in three forms:
- bedding-free manure (pure animal waste products, undigested particles of plant food);
- manure with bedding is straw, hay or sawdust, in greater or lesser quantities;
- slurry is, as a rule, manure drains, when not only manure is collected, but also water after washing premises (boxes or milking parlor).
Naturally, manure in its pure form is more profitable to purchase, since it contains only fertilizer.
manure with straw bedding
Straw manure, and even more so manure containing sawdust, has a limited area of application and is less valuable for the gardener. Although, on the other hand, straw in fresh manure absorbs urine and absorbs ammonia, reducing nitrogen losses.
But slurry is not just a highly diluted “nectar”, some of the nutrients of which will simply leak into the ground, but may contain various impurities, such as detergent residues, so when purchasing manure, choose drier fractions.
Perennials
Perennials are flowers that do not require annual planting. They need to be properly prepared for the winter season, and loosened in the spring, removing old leaves and stems. After this, the plant will begin to grow again and produce buds.
Do not forget about applying fertilizers, without which perennials, constantly growing in one place, will simply begin to starve. They only need 3 feedings:
- In early spring, as soon as the snow has melted, nitrogen is added. It allows flowers to quickly emerge from the dormant period and begin intensive growth.
- At the stage of bud formation (late May-early June). Phosphorus-containing fertilizers are relevant during this period.
- After flowering ends (August). At this stage, potassium fertilizers will not interfere with perennials. After all, from the end of summer the process of laying flower stalks for the next season begins.
Do not rush and apply fertilizer while there is still snow. Nitrogen that is not embedded in the soil will simply evaporate. Therefore, by the time the snow melts, the fertilizer will not contain any nutritional value.
Types of manure
Manure comes in different origins:
- Mullein (from cattle)
- Horse dung
- Pig manure
- Rabbit, bird, etc.
Pig manure, as a rule, is rarely used in vegetable growing and floriculture - it is not readily available, but those who keep pigs can easily use it for feeding. It should be taken into account that pig manure is highly acidic and must be heated for at least a year so as not to burn the plants.
Bird droppings fertilize the soil for up to one year, thereby being the fastest-acting remedy. Used dissolved 1:10.
Mullein is the most common and inexpensive manure; unlike horse manure, it is cheaper and more accessible.
Composition of various types of fresh manure:
- Cow: nitrogen - 0.5%, phosphorus - 0.28%, potassium - 0.6%, lime - 0.4%, pH 8.1
- Horse: nitrogen - 0.59%, phosphorus - 0.26%, potassium - 0.59%, lime - 0.21%, pH 7.9
- Pork: nitrogen - 0.8%, phosphorus - 0.58%, potassium - 0.62%, lime - 0.18%, pH 7.9
In addition, manure contains a number of minerals: sulfur, magnesium, calcium, boron, manganese, cobalt, copper, zinc, molybdenum.
How to use mullein in a greenhouse
In greenhouses, mullein can be used for “warming up”. In short, this is what they do. They dig trenches into which they dump manure. It rots within a year and can later be used for feeding.
Fertilizer is also used in the “classical” way, that is, in the form of liquid root feeding. The cost rates are the same as for fertilizing in open ground. But the deadlines are moving a little earlier. In any case, the product is best used in the early stages of the growing season.
Cow dung
Cow manure can be purchased at the nearest farm; private traders (from domestic cows) sell manure in buckets or bags. But in general, mullein can be purchased:
- fresh, just removed from a farmstead or farm, it should be of a thick consistency; if not diluted with water from wastewater, it is a non-flowing mass - bedding-free cow manure has the consistency of thick sour cream (humidity 70-75%), and straw - light holds its shape;
- half-rotted - lying in heaps for several months, considerably weathered and having lost 10–30% of the original mass and organic matter. If it was straw manure, then the bulk of the litter has rotted and crumbles easily;
- rotted manure or humus is decomposed manure; the bedding material in it cannot be distinguished either by structure or color from the total mass.
Fresh manure (mullein) is used both in spring and autumn, during the preparation of land for sowing or after harvesting the main crop and incorporating it into the soil. Mullein is first prepared in the form of a solution, diluted with water 1:10 and infused for 5 days. Manure can be used as biofuel when creating warm beds.
Semi-rotted manure can be used to prepare liquid fertilizers and for irrigation: dilute 1 kg per 10 liters of water; as mulch, placing 5-10 cm under the bushes of fruit trees and shrubs.
Rotted manure - ready-made humus is used as a component of the soil mixture for planting indoor flowers (diluted with garden soil 1:3 or 1:4), for preparing the soil in holes when planting (mixed with sand or in pure form), for mulching plantings , bushes and trees.
Why do I fertilize my garden in the spring?
I pay special attention to the spring fertilization of the plot: garden crops can quickly grow, fully develop, and form ovaries only in soil saturated with nutrients. Timely fertilization also protects seedlings from stress when moving to a permanent place and prevents diseases of young seedlings.
The most important element for spring feeding is nitrogen. It accelerates the growth of young plants and promotes the active formation of greenery. However, nitrogen is needed only for the initial stage of development. In summer, it is used only when necessary - if there is an excess of the element, the seedling goes into the tops to the detriment of fruit formation.
The second most necessary spring feedings are potassium and phosphorus. These elements are added both in mineral and organic formulations.
I recommend starting spring fertilization in early spring, but after the snow melts. Sprinkling products over snowdrifts is ineffective - valuable substances “float away” from the site along with meltwater. I do not recommend relying on the principle “the more, the better.” An excess of almost any of the useful substances in the substrate leads to the opposite effect - inhibition of growth, stunting, painful plantings, inhibition of bud ovaries, and fruit formation.
Application of manure
How to use manure depends on the crop being grown; in general, this fertilizer is suitable for almost all vegetables, fruits and berries. Only some plants accept it in any form, others do not tolerate only fresh manure, but respond well to the addition of humus.
fresh manure with sawdust
Melons (zucchini, cucumbers), as well as cabbage, potatoes and tomatoes are especially responsive to feeding with mullein. Mullein is indispensable for feeding roses, peonies, clematis, dahlias, and lilacs.
Fresh cow manure for fertilizing in root irrigation should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
Some gardeners use fermented cow slurry (it contains less nitrogen - the ammonia will evaporate). Plastic barrels are used for this. 1/3 of it is filled with manure, the rest is water. The solution must be mixed and left to ferment for a week. The fermented organic fertilizer is ready for fertilizing, but it must be diluted again with water 1:3 (3-4 buckets of water for 1 bucket of slurry). It is good to water berry plants with such fermented slurry - strawberries, raspberries, currants at the rate of 10 liters of fertilizer per 1 m² of land. Fertilizing should be done in the spring, at the time of the appearance of the first young leaves.
How to measure manure:
A standard 10 liter bucket filled to the top can hold:
- 8 kg of fresh horse manure;
- 9 kg fresh cow dung;
- 5 kg of manure on a bed of sawdust or straw
- 7 kg of humus;
- 12 kg of slurry.
What plants don't like fresh manure?
Fresh manure should not be applied to vegetables such as carrots and onions; legumes, beets, garlic, radishes, and radishes do not tolerate it well. But it is impossible to completely do without organic matter in growing these vegetables - manure is applied to the ground in the fall in a rotted form (humus).
Safety regulations
When feeding even with organic compounds, you need to remember three main rules:
- do not feed a newly transplanted or weakened plant - for the latter there should be a weak concentration of fertilizer;
- carefully study the needs of a particular variety - what it lacks and what effect will be given by the organic matter with which it is planned to fertilize it;
- Before fertilizing, you should water the flower well - if the concentration of organic matter is high, the roots will be protected by water.
Flaws
Mullein does not have many of them; they are completely covered by its advantages. Of these, the most important is a large number of pathological microorganisms that quickly multiply in its mass at above-zero temperatures outside the soil. These bacteria negatively affect plant growth, so fertilizer should be added to the soil as soon as possible.
In a fresh solution of mullein, oxidative processes are actively occurring; under no circumstances should it be used to water plants, even trees for feeding. This solution will simply burn the roots.
You should not scatter fresh mullein around the garden that has not yet rotted. It contains a large number of weed seeds, and there is a danger of sowing the garden with unnecessary weeds along with fertilizers.
Beneficial features
Mullein has many beneficial properties that are not found in other types of manure. It is for this reason that he is so valued by gardeners.
- converts insoluble mineral compounds from the soil into soluble ones, improves plant nutrition
- Thanks to its natural composition, it is completely absorbed by plants
- makes the soil lumpy, which promotes better aeration and prevents erosion by water
- the necessary microorganisms develop better in the soil, fertile humus is better formed
- improves the properties of any soil, making it fertile and of high quality.
- what is important is the low cost of the product.
If mullein is used correctly, it will protect plantings from the pathological effects of bacteria and harmful microorganisms. It is very effective and easy to use.
Precautions for use
Cow dung should be used with caution. We have already spoken about this many times, but we will say it again. Fresh fertilizer cannot be used for feeding.
When you add mullein to prepare the soil, be sure to incorporate it into the soil so as not to provoke the development of harmful microorganisms.
Also, do not forget that you need to water the liquid mullein very carefully so as not to get it on the plant. Fertilizer drops may cause burns.
To prevent the fertilizer from losing its effectiveness, it must be stored in a tightly closed barrel or bucket with a lid. It is also best to use the product as soon as possible after preparing the working solution.
Rotted manure is stored for about 4 months, and ready-made manure is stored for 6-12 months.
IMPORTANT! The more manure, the better it is stored.
What fertilizers is mullein compatible with and what is it not?
Mullein can act as a basis for complex fertilizer. It is well compatible with mineral preparations, but not with all of them. The table below provides information about the compatibility of mullein.
Compatibility table of cow manure and mineral fertilizers
| Compatible | Incompatible |
| Urea | Ammonium nitrate |
| Superphosphate, phosphorus and bone meal | Diammofoska |
| Potassium salt | Calcium nitrate |
Common mistakes
Now let's talk about the mistakes that summer residents make when using mullein.
- Use of low-quality raw materials. Cow manure can be infested with pathogenic fungi and pest larvae. If you are not sure of the quality of the drug, then it is better to abandon it in favor of mineral fertilizers.
- Too much fertilizer. Excess mullein harms plants, so do not violate the dosage.
- Use of fresh manure. This is a serious mistake that can lead to the death of cultivated plants.
Storage
Preserving mullein is quite simple; you need to follow some principles.
It is better to store it in a large pile in a cool place - this way pathogenic microbes will develop less in it.
The pile needs to be covered on top with leaves, peat or regular soil. The layer should be at least 30-50 cm, this will prevent the manure from overheating during the summer heat.
Manure should be laid in layers of 40-50 cm, the layers are also sprinkled with phosphate rock.
If slurry is used, it is stored in closed containers in dark, cold rooms.
When purchasing ready-made factory material, you should not be guided by the cheapness of the finished product. It’s better to take a more expensive and high-quality one - this will ultimately result in a better harvest.