Characteristic
The indoor lily with wide leaves is a potted plant with a gorgeous flower crowned by a long, dense stem. The similarity with the classic lily of the Liliaceae genus is based on the arrangement of the petals and the structure of the flower.
Eucharis belongs to the genus Amaryllis bulbous plants. Distribution throughout the world began in the second half of the 19th century, when the bulbs were brought from Colombia and the Amazon by botanical explorers. Lily began to be grown as a houseplant, requiring some care.
Description of the appearance of the plant:
- Bulb. The diameter of one bulb reaches 6 cm. Bulbs are often collected in groups of 2-5 pieces.
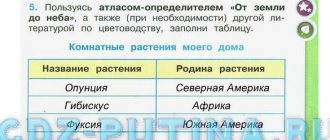
- Leaves. Large oval leaves up to 55 cm long and up to 20 cm wide are attached to the bulbs using long thick cuttings. The leaves are glossy and smooth, painted in a rich dark green color. One plant can produce 2 or 4 leaves.
- Flower. The umbrella-shaped inflorescence contains 3-10 flowers with special curling petals. Large flowers form seeds after flowering. The fruit is a leathery three-membered capsule.
The photo shows indoor lily flowers.
There are 20 species of indoor lily with wide leaves, but indoor cultivation involves the cultivation of 4 common species.
| Kinds | Description | Peculiarities |
| Large-flowered | A classic look that has large flowers with corollas reaching 12 cm in diameter. Large dark green leaves are pointed at the end point. Flower arrows extend up to 80 cm. | Representatives of the species are characterized by the presence of a persistent aroma. Flowering occurs in December, August and May. |
| White | The inflorescence is formed by 5-10 white buds, the diameter of each of them reaches 7 cm. The leaf plates are narrowed on both sides. | The species blooms at the beginning of autumn and end of spring. |
| Sandera | The species that most closely resembles the classic lily. The diameter of the flower corolla reaches 10 cm. The foliage differs from other species in its change in shade; over time it acquires a rich light green hue. | The flowering period occurs in February and September. |
| Amazonia | Representatives of the species are characterized by the presence of oval leaves without narrowing or pointed. The flowers are distinguished by smooth lines and the formation of elongated petals. | With proper care it can bloom up to 4 times annually. |
Between representatives of the species, hybrid flowers are often formed, which form separate groups.
The indoor lily is known for developing into a rich mass of foliage. Without the ability to grow foliage, the flower dies or completely stops growing. To provide the plant with this opportunity, it is necessary to create a comfortable environment.
Eucharis needs to follow some rules:
- providing lighting without direct sunlight;
- selection of nutritious soil rich in organic matter;
- introducing the necessary subcrusts to maintain strength at each growing season;
- systematic watering.
Spathiphyllum as an air purifying plant
The peace lily is a spectacular houseplant that can cleanse the air of toxic substances. It also absorbs mold spores and harmful radiation from electrical and electronic devices. Through the process of photosynthesis, the peace lily absorbs and breaks down harmful substances from the environment. In addition, it humidifies the air and converts carbon dioxide into oxygen.
Research conducted by NASA has proven that winged worms absorb dangerous compounds such as: formaldehyde, benzene, xylene, trichloroethene, carbon monoxide. The plant is an elegant interior decoration and also provides us with clean, properly humidified air, which is very important these days.
Preparation of planting material and propagation
To propagate indoor lilies, one of two methods can be used:
- Seminal. A method when seeds purchased from intermediaries are planted in prepared soil and grown in compliance with the rules of care. The method is designed to ensure that the first flowers can appear only 5 years after planting. The disadvantage of the method is the inability to predict the result.
- Bulbous. This is the most common method. Planting bulbs and propagating the mother bulb in divisions allows you to obtain an adult plant with flowers in the second year after planting. The division of bulbs is associated with taking into account the characteristics of the root system.
When choosing planting material for cultivation, it is recommended to pay attention to the appearance of the bulb:
- You should not choose bulbs whose diameter is less than 3 cm;
- each bulb should be elastic, free from spots and growths;
- after forcing, the roots sent out by the bulb look weak, but this does not affect the growth of the lily after planting.
Planting material must be properly prepared for planting. If the purchased bulbs are too dry, they are placed in water for 2 hours, then removed for further storage. Before planting, the bulbs are stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of 0 to -2°C.
The bulbs are placed in a plastic bag filled with peat or sawdust. Drainage holes must be made in the bag. Before planting, the bulbs are disinfected in a manganese solution, and damaged scales are removed from the surface.
Why did the lily turn yellow?
Lily demands attention. The indoor lily has turned yellow, a photo of the flowers can be seen below. Novice gardeners are wondering what can be done, how to save the plant? It is necessary to understand why this happened.
Causes of yellowing of leaves and stems:
- Autumn has come;
- watered incorrectly;
- the surrounding air is too dry;
- insufficient nutrition.
If the lily turns yellow in the fall, then this is normal. If there are errors in care, it is necessary to humidify the air, water it in the morning and evening, and feed it with fertilizers that contain potassium and iron.
Preparing the soil and planting site
Indoor lilies, which have wide leaves, grow on nutritious, loose soil with good drainage. The acidity of the soil is not particularly important for lilies. The normal option is to select soil with an acidity ranging from 5 to 7 PH.
Main soil characteristics:
- the basic element is turf, leaf soil or black soil;
- presence of nutrients: compost or humus;
- sand, vermiculite or expanded clay are chosen as a leavening agent;
- charcoal is added as the main element of disinfection; it helps reduce the risk of rot developing on the bulbous roots.
You can prepare the soil yourself using the traditional formula:
- leaf soil or turf - 3 parts;
- peat or compost – 1 part;
- drainage – 1 part.
All components of the mixture are calcined in the oven before cooking to avoid the development of rot or the proliferation of microorganisms.
For the plant, it is necessary to choose the right container and location. Lilies are suitable for stable, low pots in which the root system should completely entwine the earthen ball. The pots are placed on window sills or stands, where the plant will be constantly lit, but protected from direct sunlight, which can burn the leaf plate.
Landing algorithm
Bulbs are grounded in spring or fall. These times of year are traditionally considered the right time for planting or transplanting as they begin a new cycle of plant growth.
Planting involves following step-by-step instructions:
- A soil layer is poured into the pot on top of the drainage layer.
- The onion is placed in the center of the container. The voids between the bulb and the walls of the pot are filled with soil and lightly patted down.
- The soil surface is watered.
Transplantation of an adult plant is carried out according to the same scheme, but it is taken into account that the leaves may disintegrate after the bulbs are freed from the soil. To prevent this from happening, the leaves are tied in advance with strong twine. Adult plants are transplanted into a larger pot using the transshipment method. This means that the bulbs are moved to a new container with an old lump of earth.
White medicinal lily
This variety of lilies is grown exclusively for further use in perfumery and cosmetology. It is distinguished by medium-sized buds with several stamens in the center. It is grown in shady gardens and is considered one of the most demanding and high-maintenance varieties of candidum lily. The medicinal properties of its flowers have long been used to create various tinctures and lotions.
Home care
The indoor lily with wide leaves is not demanding in terms of maintenance conditions, but violation of traditional care methods can lead to stunted growth and lack of flowering. Bud formation is the goal of cultivation, so all efforts of flower growers are aimed at creating comfortable conditions for this.
Spraying, watering
Eucharis loves moist air. Spraying is carried out during the period of growth of green mass, but is completely stopped when buds appear. Moisture on the petals can cause rot and wet spots to form.
Watering should be regular and moderate. Overmoistening the soil will cause the bulbs to rot, so it is best to water only when the soil becomes dry on the upper surface area. The basic rule of watering excludes adding water in the center of the container, to the base of the stems.
Start watering the lily along the edge of the pot, using warm, settled water. The water that appears on the pan must be completely removed after watering. When the dormant period begins, the number of waterings is reduced by 2 times.
Top dressing
For abundant annual flowering of indoor lilies, systematic feeding is necessary.
They are carried out in accordance with the stage of plant growth:
- during the period of bud formation, mineral complexes with a high content of potassium and phosphorus are added;
- during the growth of green mass, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are added;
- To prevent the risk of rot and support the plant before active growth, add wood ash to the soil.
Transfer
For indoor lilies, replanting is recommended once every 3-4 years with complete renewal of the soil. Eucharis does not like too frequent replanting, but it suffers if the pot size becomes too small.
In addition, transplantation solves division problems. During transplantation, the mother plant can be divided into 2 or 3 parts. Each part is transplanted into a new container and then grown in accordance with the recommended rules.
Trimming, tying
When plants enter a dormant period, many novice gardeners make a grave mistake. They remove yellowed leaves from the pot that have lost their attractiveness. Leaves should not be removed after flowering.
Nutrients are supplied to the bulbs from fading leaf plates; they participate in the laying and development of future children. Pruning is carried out only after the flower has undergone a dormant period. The end of the period is indicated by the appearance of young shoots. Faded buds usually fall off on their own.
Heavy, dense leaves can cause the pot to tip over. To prevent loss of stability, gardeners recommend tying up the leaves or placing a support, and when a favorable period comes, planting the plants using the bulb division method.
Temperature and humidity
Despite the fact that indoor lilies love moist air, it is not recommended to specifically moisten it. In winter, you can place additional containers of water next to the pot to reduce air dryness.
The optimal temperature regime for lilies is + 20-22°C.
During the dormant period, the temperature regime is artificially reduced by moving the pot with the plant to a cooler room, but the temperature should not be reduced by more than 10-12°C. When the temperature drops below + 10 + 8°C, the lily begins to gradually stop developing.
Question about feeding
It is necessary to feed lilies 2-3 times during the summer. The very first feeding is carried out when the sprouts come out of the ground, with a solution of calcium nitrate. The next feeding should be carried out from August 1 to August 15. For it you will need:
- potassium sulfate (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water);
- hot-extracted superphosphate (10 liters of boiling water, leave 10 tablespoons of superphosphate for 24 hours, dilute the resulting concentrate in the proportion of 1 liter per 10 liters of water).
Eucharis also responds well to purchased organic fertilizers.
Possible diseases and pests, ways to get rid of them
The danger for indoor lilies is excessive waterlogging. It can create comfortable conditions for the development of root rot. This fungal disease often affects indoor lilies.
Signs of root rot:
- yellowing of leaves;
- lethargy;
- growth slowdown;
- spots form on the tips of the leaves.
Root rot prevents the growth of green mass and bud formation. Upon careful examination of the bulb, you can see the affected areas covered with spots of mold.
Treatment includes pruning leaves that are affected by rot, as well as completely treating the flower with copper-containing products. The best option would be to choose drugs such as copper sulfate, Fundazol or Topsin-M.
Red burn or stagonospora affects eucharis where temperature fluctuations often occur. The plant gets a red burn when it is overcooled or overwatered.
Signs of a red burn:
- the appearance of red spots on the leaves and buds;
- wilting of leaves and peduncles;
- curvature of buds.
The result of the disease is rotting of the bulbs and death of the plant. Timely detection of the disease allows you to cure the plant and bring it back to life. The bulb is freed from the soil, the damaged areas are inspected, and the damaged areas are cut off until healthy tissue appears.
The affected areas are treated with brilliant green or crushed activated carbon. Rotten bulbs are left on a napkin until dry for 2-3 days. Then a new substrate is selected and the planting material is replanted. To prevent the development of red burn, it is necessary to follow the rules of care, as well as treat planting material with targeted fungicides.
House lilies with wide leaves are rarely infested by pests, but if the rules of care are not followed, the following parasites may appear on the flower:
- Spider mite. Insects appear on indoor lilies when the air is dry and at high temperatures. The appearance of a spider mite can be detected by the presence of a thin cobweb on the inside of the leaf blades. The leaves must be treated with a solution of laundry soap. In case of massive damage, the plant is treated with acaricidal preparations.
- Sciarides or fungus gnats. Constant waterlogging of the soil provokes the appearance of black midges. Mosquitoes lay eggs on the bulbs, the emerging larvae feed on the juice and tissues of the bulbs, leading to complete oppression of the plant. The flower against fungus gnats is additionally treated with a solution of laundry soap or chemicals.
- Scaleworms. These are pests that develop on bulb scales. Their activity leads to curvature of leaves and peduncles and negatively affects sap flow. Scale insects are destroyed with insecticides. Treatment of soil and plants against scale insects should be done regularly.
Peculiarities
Growing indoor lilies involves taking into account nuances. The main advantage of choosing an indoor lily is its decorative properties.
In addition, there are several advantages associated with the quality characteristics of the flower:
- undemanding conditions of care;
- magnificent appearance throughout the growing season;
- presence of a persistent pleasant odor;
- the presence of lush green mass;
- air ozonation;
- creating a special indoor microclimate;
- destruction of some small insects.
The following features are considered to be the disadvantages of growing:
- Amazon lily is a poisonous alkaloid, it can cause minor harm to the skin with prolonged contact, therefore all procedures associated with transplanting and processing the plant are recommended to be carried out with rubber gloves;
- Eucharis should not be placed next to plants that will compete with it, since the indoor lily can suppress the energy of even the most powerful plant.
Even a novice gardener can cope with growing indoor lilies. The plant does not show any special care requirements. When creating comfortable conditions, it can delight owners with luxurious wide dark green leaves and magnificent buds of different shades.
Asian hybrids
The main features of these varieties are powerful growth and lush inflorescences, perfect for bouquets. Lilies begin to bloom at the end of July. Most Asian hybrids are unpretentious to conditions and reproduce easily in the first year of planting.
The Dutch variety Aphrodite is famous for its double inflorescences of 25–30 pieces each. The bush is wide, about 60 cm.
The lily of the Golden Stone variety has flowers shaped like an asterisk, they are large, up to 23 cm in diameter.
The Detroit variety is distinguished by its bright scarlet coloring of flowers. The height of the bush is 120 cm; during the first winter, the lily needs shelter.
The Lollipop variety has small (12–13 cm) but bright flowers of an interesting shape. The variety is frost-resistant (down to -20o C), blooms 70 days after germination.
Mapira lilies are unique for their color and abundance of flowering. Up to 15 buds bloom alternately on one stem. Flowers reach 17–18 cm in diameter.
The Marlene variety surprises with its ability to produce 100 buds on one bush. The flowers are small (10–13 cm), but together they form a lush bouquet. The plant needs staking.
The Spring Pink variety blooms up to 30 buds in one inflorescence. The height of the bush reaches 1 meter, so it requires mandatory garter.
The Tinos variety is very unusual. The color of the flowers is bright, multi-colored, but only appears when planted in sunny places. The height of the bush reaches 110 cm, the diameter of the flowers is 13–15 cm.
The Fata Morgana variety is the most popular of the Asian hybrids. It is valued for its unpretentiousness and lush flowering. Lily can grow in the shade and does not require shelter for the winter.
The lily bushes of the Double Sensation variety are low, up to half a meter, but bloom very profusely. The buds bloom at the end of July.