Description of fern-like plants
What is a fern, there are different versions. Scientists believe that these are direct descendants of the most ancient plants - rhinophytes. In the process of evolution, the structure of ferns has become more complex; why ferns are classified as higher plants does not surprise anyone. It confirms:
- cyclical development of plants;
- developed vascular system;
- adaptability to the terrestrial environment;
Fern in nature
By definition, a fern is a perennial plant that belongs to the genus of spore-bearing plants. To the question about a fern: is it a shrub or a herb, you can answer in the affirmative in both cases. Sometimes it is also a tree.
Additional Information. When describing ferns, one cannot help but recall their varied colors, which provide aesthetic pleasure. These plants often become a real decoration of areas. Their undoubted advantage is resistance to diseases and pests.
Important! As you know, ferns do not bloom, but in Slavic mythology, the fern flower became a symbol of eternal love and happiness. On the night of Ivan Kupala, lovers search in vain for a mythical flower.
Reproduction methods
Ferns, regardless of the variety, grown indoors can be propagated in the following ways:
- disputes;
- shoots;
- dividing the bush;
- accessory buds.
Let's consider the above methods in order.
Reproduction by spores
Fern propagation by spores is the most labor-intensive and time-consuming method of reproduction. It can be divided into several stages:
- preparation of seed material;
- planting spores;
- growing seedlings and caring for them.
Fern spores can be purchased at a specialized store, or you can try to collect them yourself on an adult plant, along with the sporangia in which they are formed. The sporangia are cut off when they become slightly brown in color. For complete ripening, they are placed in a paper envelope. After some time, the spores will ripen and spill out. This will be the seed that needs to be planted.
The next point is soil preparation. A special soil substrate for violets is best suited. It should be mixed with one part sand and three parts peat. The resulting arrogance must be brought to a uniform state, large parts of the soil must be removed and sifted well several times. Then the land for sowing spores must be disinfected. To do this, it is sent to the oven for four hours, where it is kept at a temperature of one hundred twenty to one hundred sixty degrees.
Wooden, glass or plastic containers can be used as planting containers. The main thing is to provide holes for drainage of excess liquid. Now the prepared substrate is poured into planting boxes. The thickness of the soil should not exceed four centimeters. The soil is lightly compacted and well moistened, after which spores are sown and covered with glass. The air temperature at which seedlings should appear should be constant, about twenty-three degrees. During the period of spore germination, the soil is moistened exclusively through a tray. The planting must also be regularly ventilated and condensation removed from the inside of the glass.
With proper care, fern spores germinate within a month. Visually, you can see that the surface of the substrate is covered with a green coating, reminiscent of moss. These are spores that have sprouted, but since they do not yet have a root system and are attached to the soil exclusively by rhizoid hairs, they need to be well cared for. The air temperature should be maintained at about twenty-two degrees and soil humidity. Germinated spores are left under glass until leaves appear and take root. The process of root formation and the appearance of the first leaves takes about two months. Now the seedlings need to be hardened off. To do this, they need to be opened every day for a couple of hours. After the fern has grown to five centimeters, it can be replaced by watering through a tray and spraying with a spray bottle. It must be carried out at least once a week, since seedlings must be grown in a humidified environment.
Biological classification of ferns
Types of ferns - indoor and house plants
The sheer number of fern species makes their classification difficult. Such attempts were made by ancient scientists. The proposed schemes are often inconsistent with each other. The basis for the classification of modern ferns is the structure of the sporangium and some morphological characters. All varieties are divided into ancient and modern.
The division of ferns includes the following seven classes of vascular plants, both extinct and modern:
- Aneurophytopsida are the oldest primitive group.
- Archaeopteridopsida are also ancient representatives that resembled modern conifers.
- Cladoxylopsida - there are versions that this group represents a blind branch of evolution.
- Zygopteridopsida (Zygopteridopsida or Goenopteridopsida) are a transitional group to modern species.
- Ophioglossopsids or grasshoppers (Ophioglossopsida) are modern ferns.
- Marattiopsida are perennial plants of small and large forms.
- Polypodiopsida (Polypodiopsida - perennial or less often annual plants of different sizes). They are divided into three subclasses: Polypodiidae, Marsileidae, Salviniidae.
How ferns reproduce by spores
Types of ferns and their classification
This method is most effective in the spring after the soil has warmed up. Sowing in a pot is done in autumn or early spring.
How fern reproduces using spores at home:
- Moisten the soil with a spray bottle.
- Sprinkle spores on top.
- Sprinkle a 3-centimeter layer of soil on top.
- Cover the top with glass or plastic containers, since it is necessary to create a greenhouse effect.
- When sprouts appear, you will need to remove the cover every day for 2 hours.
History of fern plant species
The history of ferns began in the era of dinosaurs - 400 million years ago. In the favorable warm and humid climate of tropical forests, ferns dominated the Earth. Some species reached 30 m in height. Over time, climatic conditions have changed dramatically. How many natural disasters had to happen for such giants as dinosaurs and tree ferns to disappear.
Reproduction of ferns - diagram and description
With all the diversity of modern ferns, they are very different from the most ancient plants, inferior to them in size and variety of shapes. But even today this is the largest group of spores - 300 genera and more than 10 thousand species. Ferns have become widespread due to their ecological plasticity and amazing reproductive characteristics.
Important! Climatic conditions favorable for ferns today remain in the tropics and subtropics, where tree ferns reach 20 m.
Curious notes about bracken
As with many plants from this family, the time of appearance of this fern on the planet is approximately 55 million years ago. Bracken is one of those ancient plants, namely lichens, that have been able to survive from ancient times to our time and have practically not changed their shape.
The plant has long been appreciated by man because of the substances that are included in its composition. Scientists have isolated not only vitamins (C, E and group B), but also flavonoids, saponins and starch, they contain proteins and tannin, glycosides and many useful microelements, including iron, iodine, manganese, calcium and others.
It is noted that it is the young shoots of bracken that are filled with the most useful components. When the fern fronds begin to increase in size and spores begin to ripen, cyanide and hydrocyanic acid take their place.
Due to the abundance of useful substances, folk healers also appreciated bracken. Dried fern shoots serve as the basis for making decoctions and are used to treat diarrhea and vomiting, headaches and colds. Such drugs help relieve nervous disorders and manifestations of hypertension, have anthelmintic properties and help with weakened immunity.
Several centuries ago, European healers used bracken to cure rheumatism and arthritis, and eliminate cramps. Its ability to stimulate the body, choleretic and expectorant properties have been revealed. If you eat young shoots, they remove radionuclides from the body, relieve stress and help resist them, increase the regeneration of human tissue and normalize metabolism.
But at the same time, as usual, there are contraindications for the use of such drugs, since the shoots may carry a small amount of poison, which can accumulate in the body. These are considered:
- childhood;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- hypotension;
- individual intolerance.
However, you should remember the symptoms of bracken poisoning: severe dizziness, vomiting and nausea, allergic reactions, problems with the liver and kidneys.
In cooking, this fern stands alongside whole foods that are used as food. If there are bracken plantings on the site, then you can harvest it for future use. If the year was lean, then such supplies helped, as they served as a substitute for bread. If you pickle young shoots, their taste is reminiscent of mushrooms, but to some they are somewhat similar to asparagus.
Important!!! Raw bracken shoots should not be eaten. Young stems are salted, boiled or soaked
Only after this can you safely eat them.
In Japan, they learned not only to salt bracken, but also to prepare sweets, pies and rare delicacies from it. In other countries, it is customary to mix crushed fern stems with flour when baking baked goods, as well as add them to salads, add them to seafood dishes, and make sauces. If you put leaves on vegetables, then in winter the fern will protect the supplies from rotting.
Prevalence in nature, examples of species
What fertilizer is needed for dracaena - choice
When and where ferns grow depends on the warmth and humidity of the area. The habitat of ubiquitous plants can be:
- lower and upper tiers of forests;
- swamps, rivers and lakes;
- ravines and damp meadows;
- rock crevices;
- walls of houses;
- roadsides.
Ostrich
In temperate latitudes you can find hundreds of herbaceous representatives of ferns. Brief overview of some types:
- Common bracken. Easily recognizable by its leaves in the shape of an open umbrella. Distributed in pine forests, suitable for consumption.
- Male shieldweed. A herbaceous plant with leaves up to 1.5 m in length, it is very rare. Shield extract is used in medicine as an anthelmintic.
- Female Kochedyzhnik. A large plant with gracefully shaped leaves.
- Common ostrich. Large beautiful fern. Due to long rhizomes it forms entire thickets. Used in landscaping areas. Boiled ostrich leaves are edible.
- Osmunda. A plant with a short rhizome and long shiny leaves native to East Asia and North America.
- Multi-row. Its leaves are dark green in color and arranged in rows.
Important! Bracken grows so quickly that its planting should be limited to various fences dug into the ground.
Suitable for home cultivation:
- Kostenets;
- Nephrolepis;
- Davallia;
- Asplenium;
- Dixonia;
- Pteris.
These plants wonderfully decorate your home interior. The Junior variety with corrugated leaves is very beautiful.
Home plant
Interesting Facts:
- Hecystortheris pumila and Azolla cariliniana are the shortest plants. Their length does not exceed 12 mm.
- Epiphytes thrive on trees and vines.
- In mountainous areas you can find Venus hair - an amazing plant with beautiful openwork leaves.
- The tree-like trunks of large ferns are used as building material in the tropics.
- Marsilea quadrifolia thrives underwater.
- Dicranopteris has leaf petioles of metallic strength.
Rare species of ferns:
- Crested shieldweed;
- Phegopteris binding;
- Brown's multi-row;
- Asplenia wall;
- The grove is multipartite.
- The Salvinia floating fern is listed in the Red Book of Belarus.
Important! Plants with beautiful leaves have decorative value and are often used in landscape design and in the preparation of floral compositions.
How to propagate fern using brood buds
Another vegetative way by which a fern can reproduce at home is by planting formed buds on the leaves in the ground. Fern-like plants have the ability to grow lateral shoots on the petioles of their leaf blades. You cannot plant an unformed bud; it must produce small roots.
Carefully separate one shoot at a time and place them in a box with substrate. Moisten the soil and place it in a warm and bright place. It is necessary to create a humid microclimate for the growth of buds, so at first they can be covered with film.
As soon as the seedlings have 2-3 leaves, you can remove the film and plant them in separate containers.
Important! You should not immediately transplant the seedlings into a huge pot. During the first years of growth, the fern will still have to be moved to larger containers each spring.
Analysis of the structure of fern plants
The ancestors of fern plants had a primitive structure. In the process of evolution it has become more complex.
Stems
The stem of ferns is underdeveloped and small in size. It is called a rhizome. Of course, tropical ferns with woody stems are an exception. The climbing rhizome can spread over long distances.
Leaves, fronds
The fern leaf is much more massive than the stem. They are not quite ordinary, they have distinctive features of structure and growth, and various shapes. More often they are dissected and feathery. Fronds are the name given to the leaves of a fern. The leaf petiole is attached to the underground part of the stem - the root or rhizome. Looking at them, it is difficult to understand where the stem ends and at what level the leaf begins. An interesting feature of the frond is its growth at the top, which is a curled and gradually unfolding curl in the shape of a snail.
Vaii
Leaf development begins in the buds underground and lasts up to two years. Only in the third year can they appear above the ground. Due to apical growth, fronds of ferns reach very large sizes.
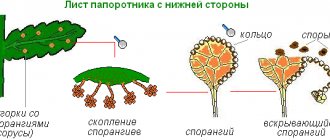
In most plants, fronds participate in the process of photosynthesis, vegetation, and at the same time in the formation of spores. Spores appear in sori, which are located on the underside of leaves in the form of single or group tubercles.
Root system
The root system consists of a powerful rhizome and numerous adventitious roots. Conductive tissue on the stem and roots absorbs water and moves it through vascular bundles to the leaves.
Reproductive organs
The life of a fern is divided into two cycles: a long asexual cycle - sporophyte and a short sexual cycle - gametophyte. The reproductive organs of ferns, sporangia, where spores are located, are located on the lower part of the leaves. Ripe spores spill out from the bursting sporangium and are carried by the wind far from the mother plant. Some scientists compare sporulation with the flowering of other plants.
Of the huge number of spores, only a part survives. The sexual phase begins when the spore germinates under favorable conditions into a haploid germ (gametophyte), which looks like a green heart-shaped plate several mm in size. On the underside of the prothallus, female and male genital organs - antheridia and archegonia - are formed. The eggs and sperm formed in them fuse in wet weather, and a zygote is formed, from which the embryo of a young plant develops - a sporophyte.
The plant can also reproduce vegetatively, when brood buds form on the stems and roots. This is important for amateur gardeners who grow certain species on their plots.
Important! It has been noticed that beautiful rare species reproduce only by spores.
How and when to divide a bush
One of the most effective and shortest vegetative methods of propagation of club mosses is the division of an adult bush. Before carrying out this procedure, it is necessary to water the bush generously with water at room temperature in order to easily pull it out of the ground without damaging the root system.
What is the structure of a fern - features of the leaves and roots of ferns
How to propagate indoor fern by dividing the bush:
- Dig holes 40-60 centimeters deep in advance. Their bottom is covered with drainage material, and the top is sprinkled with soil mixture.
- Pull the plant out of the old soil and divide it into several equal parts.
- Each of them is planted in a separate hole or pot.
Thorough root watering is carried out once a week and watered from above twice using a watering can.
Important! You cannot divide a young bush with one root rosette.
Spores on the underside of leaves
Comparison with other herbaceous plants
Pteridophytes are ferns, horsetails and mosses. They all reproduce by spores and have a common origin.
Ferns have characteristic distinguishing features from other herbaceous plants:
- They differ from algae in their rhizomes and complex leaves.
- In mosses and ferns, alternating generations of gametophyte and sporophyte occur. In mosses the gametophyte predominates, in ferns the sporophyte predominates. The presence of conducting tissue in the form of vascular bundles makes representatives of fern-like plants more adapted to a terrestrial lifestyle.
- Unlike flowering plants, they reproduce by spores and do not bloom.
Due to its rich chemical composition, fern has beneficial properties for people. Used for medicinal purposes and in cooking, suitable for pickling. Traditional medicine also did not ignore wonderful plants.
How to root side shoots
Arrows in the form of tendrils appear on the leaf blades of garden ferns, which can be rooted in the ground. Next to the plant in which this green arrow has formed, you need to place a separate container with a nutrient substrate. It is important that this container is either the same height or slightly lower than the pot with the mother plant.
Two containers are placed side by side and a side shoot with a healthy and stable tendril is bent towards the ground. Lightly dig it in with soil. If necessary, secure with a pin or wire. After this, it is thoroughly moistened and both containers are left in a well-lit place.
Interesting! After 1.5-2 months, the arrow will take root and become well established in the soil. It can be separated from the main bush and moved to another place. If necessary, transplant a small seedling into another container.
Brood buds form on leaf blades