On the one hand, wild radish is a malicious poisonous weed, on the other hand, it has medicinal properties and is often used in folk medicine, and the plant also produces nectar and pollen in sufficient quantities for bees to collect, that is, it is a good honey plant. Read more about the characteristics of wild radish, its botanical characteristics, classification, benefits and harms.
Radish Application
Collection and processing of medicinal raw materials
What family does the pea belong to: vegetable, fruit or legume, description of the plant?
Medicinal raw materials are root vegetables, especially black ones, and seeds. Root crops are dug up in the fall, shaken off the ground and dried a little in the air. Store in the basement in wooden boxes with dry sand all winter.
Application in official and folk medicine
Radish preparations stimulate appetite, stimulate the secretion of digestive juices, have a diuretic and choleretic effect, affect metabolism, are an expectorant, sedative and antimicrobial agent.
In medicine, radish is used for acute and chronic gastritis, especially when the secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract is reduced. Due to the large amount of fiber, root vegetables stimulate intestinal motility and increase the secretion of digestive juices. This allows them to be successfully used for chronic inflammation of the small and large intestines, chronic hepatitis and developing cirrhosis of the liver.
The combination of beneficial substances contained in radish helps reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, so root vegetables are an indispensable means for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis of the heart and brain vessels. When treating, it is recommended to combine radish juice with apple juice.
This root vegetable is also known as a good diuretic, especially for kidney and bladder stones. Its juice is used for acute and chronic diseases of the bronchi and inflammation of the nasopharynx. In this case, radish juice is mixed with honey or sugar in a ratio of 1:3. Locally, the juice is prescribed as a rub for rheumatism, radiculitis and neuralgia. To do this, three to four parts of radish juice are mixed with two parts of honey and one part of vodka. This rubbing can be used for a long time; Store it in the refrigerator in a well-closed porcelain or glass container.
Juice and grated radish or crushed seeds are used to treat purulent wounds, eczema and non-healing skin ulcers.
Radish juice with carrot and beet juice has long been considered a good remedy for treating anemia. To do this, raw root vegetables are grated on a fine grater, mixed in equal quantities, the juice is squeezed out through a canvas cloth, poured into a clay container and placed in a preheated stove or oven for 2-3 hours. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 2-3 months.
Features of cultivation
The plant is quite unpretentious, however, when specifically growing wild radish for medicinal purposes, some features are taken into account.
Basic landing rules
When planting wild radishes, adhere to the following rules:
- Previous cultures. Radishes are not planted after crops of the same family - Cruciferous plants: radishes, cabbage, daikon and other representatives. This is due to the possible presence of a cross-shaped flea beetle at the planting site, which infects plants of this family.
- Soil composition. To get a good harvest, add humus aged 2-3 years and dilute it by a quarter with wood ash.
- Disembarkation time. Field radish consistently produces 2 harvests per season. The first harvest does not have good shelf life. This quality distinguishes the autumn harvest. The second planting is carried out in the first ten days of June, in the southern regions - at the end of June.
Features of agricultural technology
When carrying out agricultural activities, the following rules are adhered to:
- Place and method of planting. Culture loves well-lit places. When planting, seeds are planted 2-3 cm deep into the soil.
- Thinning and loosening. After the first shoots have appeared, the soil is loosened, and the shoots are thinned to a distance of 5-6 cm. When the shoots become stronger, a second thinning is carried out to a distance of 15 cm.
- Feeding. When 3-4 leaves appear, the first feeding is done. In this case, exclusively mineral fertilizers are used. The next feeding is carried out a month after the first. As a top dressing, the following is diluted in 10 liters of water:
- urea - 20 g;
- superphosphate - 60 g;
- potassium chloride - 15 g.
- Watering. Wild radish is demanding when it comes to watering. Even short-term exposure to dry soil negatively affects the quality of the crop. Watering is carried out regularly, depending on weather conditions, preventing the soil from drying out.
Features of growth and reproduction
The germination depth of wild radish seeds is 2-5 cm. Temperature fluctuations, especially at an interval of 12°C, promote their germination after a dormant period, which lasts on average from 6 to 8 months. They remain viable in the ground for up to 10 years. To germinate, it is enough for them to warm the soil to 2-4°C after overwintering.
Radish reproduces only by seeds. They usually spread close to the mother plant. Experts explain the spread of the weed over greater distances by the fact that the grain of cereal crops - wheat, oats, rye - was contaminated with weed seed material.
Possible reasons for restricting access:
What family do potatoes belong to: description, video and photo
Access is limited by court decision or on other grounds established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A network address that allows you to identify a site on the Internet is included in the Unified Register of domain names, page indexes of Internet sites and network addresses that allow you to identify sites on the Internet containing information the distribution of which is prohibited in the Russian Federation.
A network address that allows you to identify a site on the Internet is included in the Register of domain names, indexes of pages of sites on the Internet and network addresses that allow you to identify sites on the Internet containing information distributed in violation of exclusive rights.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Structure
This is an annual herbaceous weed. The root system is taprooted with a powerful shortened strong root. The stem is branched, relatively tall, and can reach a height of 30 to 70 cm. In the lower part, the stem is thin and covered with stiff hairs. The arrangement of leaves on the stem is alternate. The leaves are simple, lyre-shaped, pinnately dissected with 4-6 rounded lobes.
Wild radish flowers usually have yellow, less often white or purple petals, collected on the tops of the main and lateral shoots in inflorescences - racemes. Wild radish flower formula: 4 petals and 4 sepals arranged in a cross, six stamens and one pistil. The flowering period of this plant lasts throughout the summer and early autumn.
In autumn, the fruits ripen - dense pods 4-8 cm long and 0.5 cm in diameter. A characteristic feature of the structure of wild radish pods is that when ripe they are divided into several segments, each of which contains one seed. The embryo of a fallen seed has two protective layers: the peel and the pericarp. The seeds contain mustard oil, so after the fruits ripen, field radish becomes dangerous for farm animals.
Meaning. Wild radish is an excellent honey plant. Many pollinating insects feed on the nectar of its flowers and spread pollen. This type of radish has also found application in medicine.
In agriculture, there is a stubborn fight against this weed. Wild radish spreads quickly with insufficiently cleaned cereal seeds. Control measures include thorough grain cleaning, autumn plowing, stubble peeling, weeding of crops, inter-row cultivation of row crops.
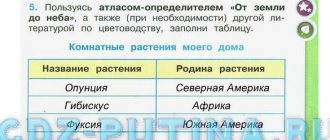
Helpeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeing Please) Using herbarium specimens, describe 2-3 plants of the cruciferous family. When describing, follow the following plan. 1) note the features of the external structure of the root. Determine the type of root system 2) While studying the shoot, note the features of the external structure of the leaf, the type of venation, the type of leaf arrangement, and the features of the external structure of the stem. 3) Determine whether the plant has a single flower or an inflorescence. Determine the type of inflorescence 4) While studying the structure of a flower, note the structural features of the calyx, the structural features of the corolla, the number and arrangement of stamens, the structural features of the pistil, the number of pistils in the flower. 5) Study the structure of the fetus. Note the structural features. Determine the type of fruit 6) Indicate which class and family the plant you described belongs to. Based on what signs did you determine this?
Read also: Installation of gas boilers
Benefit
What type of fruit is potato?
Wild radish seeds and tubers have wide medicinal uses. This is explained by the high content of thioglycoside glucobrassicin and flavonoids in its tubers, as well as a large amount of fatty oil in its seeds. In addition, it contains many useful vitamins and microelements: iodine, iron, phosphorus and potassium. Radish has strong antibacterial and bactericidal properties, therefore it is widely used to treat various skin diseases. A decoction of its seeds helps with tumors and rheumatoid arthritis. To do this, you need to pour 1 teaspoon of seeds into 1 tbsp. water. The resulting mixture is boiled and left to infuse for about 2-3 hours. The strained tincture is taken three times a day, 1-2 tbsp. spoons both before and after meals.
The tubers of the weed plant perfectly restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, wild radish fruits are very useful for people suffering from urolithiasis. To prepare the medicine, you need to select a fairly large radish and make a small depression in it. Sugar or honey is added to it to stimulate the separation of bitter juice and soften its taste. The resulting juice should be taken once a day in the amount of 2-3 tbsp. spoons A similar medicine is used for respiratory diseases and to remove mucus from the lungs. When properly prepared, such a medicine can be more effective than various tinctures and sprays purchased at the pharmacy.
In addition to preparing various decoctions, wild radish leaves can be used for food by making a salad from them. For this you will need:
- 200 g radish leaves;
- 150 g green onions;
- 50 g parsley;
- 50 g dill.
For the sauce you will need:
- 2 eggs;
- 0.5 tbsp. low-fat sour cream;
- 1 tbsp. spoon of vegetable oil;
- 1 teaspoon apple cider vinegar;
- salt and sugar to taste.
All greens must be thoroughly washed and dried with a paper towel, and then finely chopped into a deep bowl. Egg yolks are beaten with sour cream and vinegar, after which butter, sugar and salt are added to the sauce. This salad is served in portions, spread out on large dried pieces of white bread.
At the same time, people suffering from gastritis and ulcers are strictly prohibited from eating wild radish.
Externally, wild radish is very similar to ordinary domestic radish, which can be found in almost every summer cottage, so it is easy to confuse them. However, during the flowering period, the weed becomes very toxic due to the accumulation of mustard oils in its inflorescences. Its stems and leaves are also saturated with poison, which can only be removed by drying them thoroughly. If you add such greens to a salad, you can easily get serious health problems.
And the root of a wild plant is poisonous throughout the life of the weed, so it cannot be consumed internally, regardless of the radish flowering.
The first signs of poisoning are changes in the color of urine from yellow to bright orange and severe nausea and even vomiting. Intoxication may cause dizziness and increased heart rate. If the necessary measures are not taken in a timely manner, dangerous changes in the kidneys and adrenal glands can occur. In case of poisoning, you should act according to a certain algorithm.
- First of all, it is necessary to perform a complete gastric lavage as early as possible. To do this, you can use either ordinary boiled water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- The second thing to do is to perform an enema with plain water or the same solution of potassium permanganate. This is necessary to completely cleanse the intestines of toxic weed residues.
- For severe pain in the heart and obvious arrhythmia, you should take validol or nitroglycerin.
- To reduce side effects on the stomach, some time after cleaning it, it will be useful to drink 1-1.5 liters of thick jelly. It envelops the gastric walls and protects them from inflammation.
- A heating pad with cold water or a wet towel is placed on the stomach, after which an ambulance is called. Even if the pain and pain have already passed, and the nausea has subsided, it will be better if a specialist examines the victim.
What is the danger
Wild and cultivated radishes are very similar to each other, but the inflorescences of the wild relative are poisonous. When wild radishes bloom, they become very toxic. Only after the stems and leaves are thoroughly dried will they lose their poisonous qualities.
When the plant blooms, its above-ground parts (stems, leaves and flowers) produce mustard oils, which are a source of toxic substances. If during flowering wild mustard greens or flowers are added to any culinary dish, then eaters can get seriously poisoned.
Botanical description
Wild radish is an annual plant from the cruciferous family; its Latin name is Raphanus raphanistrum. The plant is considered a weed and is widespread throughout our country, especially in the southern and eastern regions.
The weed grows in abandoned areas, roadsides, crop fields, pastures, pond banks, floodplains, and open forests in temperate, subtropical, semi-arid, and sometimes tropical regions.
Roots, leaves and flowers
An annual herbaceous plant with a vertically growing herbaceous stem usually reaches 40-60 cm in height. The root system is shallow and weakly branched. Wild radish produces a basal rosette of large, deeply lobed leaves during the early stages of growth. Its smaller and narrower upper leaves are alternately arranged on the stem and have fewer lobes than the lower leaves of the plant.
The annual may have white, pale yellow, lilac, pink or, rarely, purple flowers (18-40 mm across) that have four petals. Flowers are arranged in loose, elongated clusters at the tips of herbaceous branches. The annual blooms in early summer.
Wild radish stems are round or slightly lanceolate and range in color from bluish-green to purple. The stems may be unbranched or form several long branches near the base of the plant.
The leaves are green or bluish-green in color, covered with small, stiff hairs and slightly rough to the touch. The lower (rosette) leaves of the plant are large (from 15-30 cm in length and 5-10 cm in width), located higher along the stem, and have narrow and jagged edges. The higher the top of the plant, the smaller and sparser the leaves. Reproduction
- At the end of flowering, elongated seed pods form on the plant (3-9 cm in length and 3-6 mm in width). The testes are attached to the wild radish by stems 1-3 cm long and end in a tapering “beak” (1-3 cm long). The seed pod is divided into several segments. The testes resemble a pod in which the pea seeds are found. The seed pod is green or purple in color when immature and turns yellowish brown or grayish in color as it matures.
- When the seed pods are fully ripe, they easily split into 3-10 segments (3-7 mm long and 2-5 mm wide). Moreover, each segment contains one seed. The seeds are almost round in shape, their diameter is from 1.5 to 4 mm, and are red or yellowish-brown in color. During the season, from 150 to 300 seeds ripen on an annual plant. Seeds that fall to the ground germinate only a year later, after winter stratification under natural conditions.
- Wild radish reproduces only by seeds, which are spread some distance from the mother plant by wind, water, animals and humans. It is believed that the spread of the seeds of this weed over long distances occurs due to weed-contaminated grain (wheat, oats, rye).
Wild radish (Raphanus raphanistrum) is primarily a weed found in agricultural lands and near human habitation. The annual plant is called a good honey plant; the calyxes of the flower stalks contain enough nectar and pollinating insects are attracted by the sweet, far-reaching aroma. In agriculture, this weed is regularly controlled in cultivated fields, since vegetable crops or grains take longer to germinate than wild radish seeds. If measures are not taken in time and the unwanted inhabitant of the field is not destroyed, the weed will grow and will not allow bread or potatoes to grow. In private farms, gardeners destroy wild radishes using hand weeding; in large areas, their reproduction is kept under control using herbicide treatments.
How to get rid of a weed?
Farms that suffer from the invasion of wild radishes carry out the following measures to destroy them:
- The weed seedlings are destroyed at the “white thread” stage - this stage begins in early spring, when rare sprouts appear on the soil surface, but in the ground the seeds are already sprouting en masse. To destroy most of the weeds, it is enough to loosen the soil to a depth of 5 cm with a hoe or rake.
- They dig up the soil in the autumn.
- Alternate sowing of winter and row crops.
- Use approved herbicides.
- If the area of the plot is small, then the weeds are removed manually.
Wild radish causes great harm to agriculture, so they are constantly fighting against it.
To see what wild radish looks like and its taste, see the following video:
Wild radish is a weed plant that is not devoid of beneficial properties. Wild radishes are rarely grown specially; often, on the contrary, they try to get rid of them, since they prevent many crops, especially cereals, from growing. When using wild radish for medicinal purposes, strictly follow the recipe to avoid possible poisoning.
0
0
Copy link
Raphanus raphanistrum L
Systematic position.
Brassica family Brassicaceae Burnett (Cruciferae Juss.), genus Cabbage Raphanus L.
Biological group.
Morphology and biology.
Plant 20-60 cm tall, covered with stiff hairs. The stem is straight. The leaves are lyre-pinnately dissected, with 4-6 unequally toothed oblong-ovate lobes and a larger apical lobe. The inflorescence is a raceme. The flowers are actinomorphic, 4-membered, the petals are arranged crosswise, usually yellow, less often white or with a purple tint. The fruit is a pod, segmented, the lower part of the pod is clear-shaped, longitudinally grooved, the upper part is elongated into a long conical spout. The pod is woody, glabrous, straw-yellow; when ripe, it splits along transverse false partitions into separate segments. The seeds are oval-spherical, reddish-brown, their surface is reticulate, matte. Seeds enclosed in shells retain germination up to 18% when the segments pass through the digestive tract of animals. Blooms in May-September, bears fruit in July-October. Maximum fertility up to 2500 seeds. The minimum temperature for seed germination is 2-4°C. Seeds germinate from a depth of no more than 3-4 cm in the second year. The viability of seeds lasts up to 10 years or more. In the phases of germination and the beginning of fruiting, it can withstand frosts down to – 11° C, but does not overwinter.
Spreading.
Western Europe, with the exception of northern Scandinavia, Asia Minor, Syria, introduced into North America. Distributed throughout the European part of b. USSR, rarely in the Caucasus, Siberia and the Far East.
Ecology.
Prefers loose soils. It grows especially abundantly in wet years with cold spring. The fruits ripen before early grain crops are harvested; most of them fall off and clog the soil; some fall into the grain during harvesting. Distributed mainly with cereal seeds.
Economic importance.
It infests mainly spring crops in the Non-Chernozem zone b. USSR, occurs in the southern regions, but loses its significance as a weed. It is also found in fallows, like ruderals - along roads. Protective measures: early peeling and plowing in autumn, use of rotted manure. Cleaning seed material on triremes.
Literature:
Zotova A.P. Weeds and their control. Leningrad: Lenizdat, 1971. P. 60. Korsmo E. Weeds of modern agriculture. M.-L.: State. publishing house kolkh. and sovkh. Literary, 1933. pp. 115-116. Nikitin V.V. Weeds of the flora of the USSR. Leningrad: Nauka, 1983. 454 p. The main weeds and field plants of agricultural crops in the Leningrad region. VIR World Collection Catalog, vol. 468. Ed. Agaev M.G. Leningrad: VIR, 1988. pp. 44-46. Weeds of the USSR, vol. 3. Ed. Keller B.A. Leningrad: USSR Academy of Sciences, 1934. pp. 67-69. Ulyanova T.N. Weeds in the flora of Russia and other CIS countries. St. Petersburg: VIR, 1998. 344 p. Flora of the USSR, vol. 8. Ed. Komarov V.L., Bush N.A. M.-L.: USSR Academy of Sciences, 1939. P. 494-495.
Taxonomy and range
The type of wild or field (coastal) radish includes:
- to the genus - Radish;
- family - cabbage (cruciferous);
- class - dicotyledonous;
- department - flowering plants, angiosperms;
- kingdom - Plants.
Radish grows in the European part of the former USSR, in the non-chernozem forest belt. The weed is found in Africa, Asia, and also in European countries. Favorite places of growth are meadow thickets, roadsides and abandoned areas.
Beneficial features
The main reason for changes in health during this period is an acute lack of vitamins. This deficiency can be compensated for with the help of pharmaceutical vitamin complexes or obtained mineral nutrients from a weed plant - wild radish.
Useful substances found in this plant:
- minerals;
- essential oils;
- vitamins;
- potassium;
- phosphorus;
- iodine;
- iron;
- calcium;
- sodium salts
Its aerial parts (stems and leaves) contain vitamin C, and ripened seeds are a source of vegetable oils, the percentage of which in ripened wild radish seeds reaches 32%.
Beneficial features:
- antimicrobial;
- bactericidal;
- expectorant;
- antiscorbutic;
- antianemic;
- antibacterial.
The plant is a natural antibiotic; taking it in the right doses does not cause side effects or contraindications, which is the problem with many pharmacological drugs.
Did you know? The ancient Greeks considered the radish to be the king vegetable and cast it life-size in gold. It was an offering to the god Apollo at the annual Delphic celebrations.
The plant promotes:
- rapid metabolism (metabolism);
- increases the body's production of saliva and gastric juice several times;
- works as a diuretic, thereby eliminating swelling;
- improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- removes toxins from the body, preventing them from entering the liver.
ethnoscience
This weed has long been used in folk medicine. On its basis, medicinal drugs are prepared, with the help of which many health problems are eliminated.
What diseases are treated in folk medicine with wild radish:
- poor vision;
- cough;
- anemia;
- colds;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- arthritis or radiculitis;
- malaria;
- scurvy and bleeding gums;
- sexual impotence in old age;
- poorly healing (inflamed, festering) wounds;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- prevention of atherosclerosis;
- decreased lactation during breastfeeding.
Important! Self-medication with dangerous herbs is unacceptable! You should definitely seek advice from your local physician. Who should not use it: Who should not use:
Who should not use:
- patients with gastritis;
- people diagnosed with a stomach ulcer or duodenal ulcer.
Wild radish leaf salad recipe
Salad ingredients:
- wild radish leaves - 200 g;
- green onion feathers - 150 g;
- parsley leaves - one bunch;
- young dill greens - one bunch.
Ingredients for the sauce:
- eggs - 2 pcs.;
- sour cream - 0.5 cups;
- sugar - 1 tbsp. spoon;
- salt - 0.5 teaspoon;
- sunflower oil - 1 tbsp. spoon;
- vinegar - 1 tbsp. spoon.
Preparing the salad: all the greens are washed under running water and laid out on a cloth or towel to dry. Next, the greens are finely chopped, placed in a deep salad bowl and mixed thoroughly, after which the contents of the salad bowl are poured with whipped sauce.
Prepare the sauce: the raw yolks of two eggs are mixed with sour cream, sugar, sunflower oil, vinegar and salt are added.
Did you know? There are Asian varieties of radish: Chinese radish (lobo), its taste is similar to the taste of ordinary radishes, and Japanese radish (daikon) - this one differs from all varieties by the record length of its thick root. Japanese radish can reach a weight of three kilograms.
This weed plant is an excellent honey plant - a source of nectar and pollen for working bees. Beekeepers try to take the apiary to a summer camp near places where wild radish grows in abundance. Some enthusiasts even deliberately scatter pre-collected seeds of this plant in places of future honey collection.
Wild radish is a storehouse of minerals and vitamins; it can and should be eaten. But you should always remember the existing danger of poisoning people and animals by this plant.
Origin
Radish has been known since time immemorial. The attitude towards this root crop was twofold. The ancient Egyptians considered it an “unclean” vegetable because it was part of the diet of slaves who took part in the construction of the pyramids.
The ancient Greeks, on the contrary, valued this root vegetable and presented it as a gift to the god Apollo at the Delphic Games, and also cast it in gold. In addition, ancient Greek healers classified the root vegetable as a medicine and prescribed it to patients.
Wild radish is known in the western part of the country as field radish, in the eastern regions as coastal radish. In addition, it has many popular names:
- gorlyupa;
- chicken nap;
- field mustard;
- jaundice;
- jaundice;
- blister grass;
- redeshnik;
- saffron milk cap;
- fierce;
- rapeseed;
- field horseradish;
- borbora.
Radish care: fertilizers, watering, weeding
The plant is quite unpretentious. Caring for radishes consists of watering, weeding, loosening and hilling. Once a week it is necessary to water the plantings abundantly. It is also necessary to thin out the plants. The first time this is done is when the first leaves appear. Then after 20 - 30 days. The distance that should be between plants depends on the variety. For early varieties - a distance of 6 - 8 cm. And for late varieties - a distance of 12 - 15 cm.
You can feed vegetables only with mineral fertilizers. Organic fertilizers have a bad effect on the quality of root crops and their keeping quality. Fertilizers can be applied in both dry and liquid form. However, dry fertilizers can only be applied when the soil is moist.
Usually two feedings are carried out. The first time when the first leaves appear. The second is 20 - 30 days after the first, when the root crop begins to ripen. 60 g of superphosphate, 20 g of urea and 16 g of potassium chloride are dissolved in one bucket. For 15 - 20 meters of one row, use one bucket of solution. When fertilizing in dry form, 20–15 g of superphosphate, 5–10 g of potassium chloride and 5–10 g of urea are added per 1 m2.
Plantings should be protected from cabbage leaf beetle, spring cabbage fly, flea beetle, cabbage moth, cabbage aphid, clubroot, cabbage mosaic, slugs, rapeseed flower beetle, and blackleg symptoms.
Agrotechnics of cultivation
Radish: calorie content, benefits and harm, recipes for weight loss
The crop is a cold-resistant plant, but despite this, the sowing time must be calculated so as not to get a flower shoot or a small hard root instead of a root crop. The choice of site also matters.
Site preparation
When choosing a place for a ridge, you need to take into account the predecessor crops. It is impossible to plant any rare variety after cruciferous vegetables (rutabaga, cabbage, salads, radishes) - they have common diseases and pests. It is preferable to plant after nightshades, cucumbers, and peas.
They begin to prepare the bed for early varieties in the fall. First, they dig it shallowly (5-6 cm) to allow the weeds to sprout, then, when they sprout, they dig it a second time onto the bayonet of a shovel. When digging into low-fertility soils, it is recommended to add rotted humus, mature compost (4-6 kg/1/m²), ammonium nitrate (15-20 g/1 m²), superphosphate (20-30 g/1 m²), potassium chloride (15 -20 g/1 m²).
In the spring, after the soil has dried, all that remains is to loosen it by adding 5-10 g of potassium and phosphorus fertilizers per square area. If planted in dense, poorly dug soil, the root crop will grow crooked.
The preparation of the bed for planting late varieties is carried out 1.5-2 weeks before sowing, when space is freed up after other vegetables.
Carrying out sowing
Seed material is prepared in advance. First, the seeds are sorted, leaving large and medium ones, then kept in a saline solution (50g/1 l) for 5-10 minutes, those that have settled to the bottom are washed and dried. Shortly before sowing, soak in a manganese solution (0.2 g/1 l) for 15-24 hours.
The timing of sowing depends on the growing season and variety. Early varieties for summer use are sown in mid-April-early May, winter varieties later - mid-to-late June, when spinach and dill are harvested, and Chinese and Japanese - in the last days of July. Late varieties cannot be planted early - with long daylight hours and high temperatures, they throw out the peduncle, the root crop stops growing and becomes tough.
Planting options (planting depth - 2-3.5 cm, seed consumption rate - 0.3-0.4 g/1 m²):
- on ridges in two rows, row spacing – 20-50 cm;
- on ridges in 3-4 rows, row spacing - 25-40 cm;
- on a flat surface in one line, row spacing – 45 cm.
How to care
In order for the radish to grow large and even, you need to follow the rules of care that meet the requirements of the plant:
- Thinning, loosening. The row spacing is loosened to a depth of 4-6 cm. With deep loosening, there is a possibility of root damage; weed seeds from the deep layers move to the upper layers, germinate, and prevent the seedlings from developing.
- The first time is thinned out in the phase of two leaves, leaving a distance of 8-10 cm between the seedlings, the second time - if there are four leaves, the distance should correspond to the variety. For early ones - 10-12 cm, for late ones - 15-20 cm. Seedlings removed during the first thinning can be replanted in an empty place. When plantings are dense, the plant throws out a peduncle.
Watering, fertilizing. Normally, the soil should be slightly moist, not wet, and there should be no sudden changes in its condition. If the soil is either dry or wet, voids form in the root pulp. Consumption rate – 20-30 l/1 m². Feed twice during the season. For the first feeding, use an infusion of greens, diluted in a ratio of 1:3, consumption – 10 l/3-4 m². The second time, mineral fertilizers are used in dry or liquid form (calculation is given for 3-4 m²): potassium chloride (10 g), superphosphate (10-15 g), ammonium nitrate (10 g). You can use complex formulations at the rate of 20-30 g for the same area.
Prevention of diseases and pests. Timely prevention will help avoid infection by infections (fomoz, clubroot, downy mildew, bacteriosis, black mold), and prevent damage by insects (various types of butterflies, fleas, aphids, bedbugs, mole crickets, etc.).
Advice to a summer resident: How to protect your garden from aphids
What can be done:
- observe crop rotation and sowing dates;
- lime acidic soils;
- dig the soil deeply in the fall (pest larvae and pathogens moved higher will die in frost);
- loosen and weed in a timely manner;
- clear the area of plant debris.
Wild radish morphological description - Summer resident's guide
Veronica spicata (spikelet): description, planting, care, use in folk medicine
Wild radish is a herbaceous, poisonous annual plant that colonizes fields as a weed.
It is unpretentious to climate and soil, distributed over almost all continents, most often found in the forest zone of Europe, as well as in meadows, along roads, wastelands and even on city lawns.
It germinates, as a rule, in spring and summer, but it also happens in autumn, at an air temperature of +2-4 degrees C.
Field plant - wild radish
The Cruciferous family are plants that are pollinated by insects. Therefore, many of them smell and have nectar. Our herbaceous plant belongs to this family.
It has a fairly high, splayed, straight stem (reaches 50-60 cm in height), covered with stiff hairs. The leaf is lyre-shaped and grows alternately. The root system is in the form of a shortened root.
The color of the flowers is white, yellowish, rarely purple-white. The weed's petals grow crosswise and consist of one pistil and six stamens. The length of the fruit, which ripens in the fall in the form of a pod divided into 5-10 segments, can reach 8 cm.
The seeds are in oval-shaped pods of a reddish hue.
Scientists have proven that in soil a seed can maintain its viability for up to 10 years. Wild radish blooms in May-September and bears fruit in July-October. In the phases of germination and the beginning of fruiting, it can withstand frosts down to –119deg;C, but does not overwinter.
The plant does a lot of damage in fertile fields; it spreads well throughout the beds, preventing vegetable crops from germinating.
Wild radish is endowed with poisonous properties when in bloom, and only loses them when dried.
In some countries, for example in England, the stems of this plant are used for food in the form of salads, soups and even seasonings, but after treatment with heat they are not suitable for this, as they have a bitter taste. When dried, they are used to make seasonings.
Closer to autumn, when the pods ripen, the weed becomes dangerous for animals: by secreting mustard oil, it can lead to acute damage to the gastrointestinal tract. The plant looks similar to field mustard. Poisoning of rabbits is possible after feeding grass from the fields.
However, radish has excellent honey-bearing properties - it provides a large amount of nectar and pollen for bees. In folk medicine, a decoction of it was used as an expectorant. Beneficial properties include the content of vitamin C in the aerial part of the weed, and in the seeds - 20-32% fatty oil.
Finally, we will share with you an interesting and simple dish that can be prepared from this plant.
Wild radish salad recipe
Wash the leaves (200 g), cut them, put them in a deep plate. Grind the yolks (2 eggs) with sour cream (1/2 cup), sugar (1 tablespoon), vinegar (1 tablespoon), sunflower oil (1 tablespoon) and salt. Beat the whole mixture and pour it over the leaves, sprinkle chopped parsley, dill and onion on top.
Conclusion
Now you know what wild radish looks like - you can see a photo of it in our article. You know how and where it grows and what the properties of this plant are.
Our ancestors slept differently than we do. What are we doing wrong? It’s hard to believe, but scientists and many historians are inclined to believe that modern man sleeps completely differently than his ancient ancestors. Initially.
20 photos of cats taken at the right moment Cats are amazing creatures, and perhaps everyone knows this. They are also incredibly photogenic and always know how to be in the right place at the right time.
Top 10 Broke Stars It turns out that sometimes even the biggest fame ends in failure, as is the case with these celebrities.
7 Body Parts You Shouldn't Touch with Your Hands Think of your body as a temple: you can use it, but there are some sacred places that you shouldn't touch with your hands. Research showing.
Contrary to all stereotypes: a girl with a rare genetic disorder conquers the fashion world. This girl's name is Melanie Gaydos, and she burst into the fashion world quickly, shocking, inspiring and destroying stupid stereotypes.
Classification
Taxonomy
| Top down. Sheet. Flower. |
White Polish. white Polish mushroom: characteristics, beneficial properties and cooking options
Species Radish
belongs to the genus Radish ( Raphanus
) family Brassicaceae
,
order
Brassicales
.
| 14 more families (according to the APG II System) | from 2 to 9 more types | |
| order Brassicas | genus Radish | |
| Department Flowering, or Angiosperms | Brassica family | Field radish |
| 44 more orders of flowering plants (according to the APG II System) | about 330 more births |
Representatives
Within the species there are a number of subspecies:
Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. landra (Moretti ex DC.) Bonnier & Layens
Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. maritimus (Sm.) Thell.
- Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. microcarpus (Lange) Thell.
- Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. raphanistrum
- Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. rostratus (DC.) Thell.
Features of cultivation
The plant is quite unpretentious, however, when specifically growing wild radish for medicinal purposes, some features are taken into account.
Basic landing rules
When planting wild radishes, adhere to the following rules:
- Previous cultures. Radishes are not planted after crops of the same family - Cruciferous plants: radishes, cabbage, daikon and other representatives. This is due to the possible presence of a cross-shaped flea beetle at the planting site, which infects plants of this family.
- Soil composition. To get a good harvest, add humus aged 2-3 years and dilute it by a quarter with wood ash.
- Disembarkation time. Field radish consistently produces 2 harvests per season. The first harvest does not have good shelf life. This quality distinguishes the autumn harvest. The second planting is carried out in the first ten days of June, in the southern regions - at the end of June.
Features of agricultural technology
When carrying out agricultural activities, the following rules are adhered to:
- Place and method of planting. Culture loves well-lit places. When planting, seeds are planted 2-3 cm deep into the soil.
- Thinning and loosening. After the first shoots have appeared, the soil is loosened, and the shoots are thinned to a distance of 5-6 cm. When the shoots become stronger, a second thinning is carried out to a distance of 15 cm.
- Feeding. When 3-4 leaves appear, the first feeding is done. In this case, exclusively mineral fertilizers are used. The next feeding is carried out a month after the first. As a top dressing, the following is diluted in 10 liters of water:
- urea - 20 g;
- superphosphate - 60 g;
- potassium chloride - 15 g.
- Watering. Wild radish is demanding when it comes to watering. Even short-term exposure to dry soil negatively affects the quality of the crop. Watering is carried out regularly, depending on weather conditions, preventing the soil from drying out.
Features of growth and reproduction
The germination depth of wild radish seeds is 2-5 cm. Temperature fluctuations, especially at an interval of 12°C, promote their germination after a dormant period, which lasts on average from 6 to 8 months. They remain viable in the ground for up to 10 years. To germinate, it is enough for them to warm the soil to 2-4°C after overwintering.
Radish reproduces only by seeds. They usually spread close to the mother plant. Experts explain the spread of the weed over greater distances by the fact that the grain of cereal crops - wheat, oats, rye - was contaminated with weed seed material.