A phytolamp for orchids is actually very important for plants, since it plays an important role in their development and subsequent flowering. Often the gardener does not have the opportunity to transfer the entire home oasis to the windowsill located near the window on the south side of the house. Also, plants kept in an apartment see very little light even on a clear day in summer, and besides, on the other side of the window, nearby houses or trees successfully cover it. That is why a variety of lamps have been made that can compensate for the lack of sunlight for house plants.
However, how to decide on the type of lamp to satisfy all the needs of such a capricious exotic plant as an orchid? To do this, please review the information provided below.
Description and main characteristics of the device
There are many different lamps for lighting a flower. How to choose the right orchid?
Energy saving lamps (CFL)
- Their advantages over conventional incandescent lamps are obvious: They consume 4-5 times less energy. And the return is higher;
- Long warranty periods;
- Security is higher. Short circuits are very rare.
- Blue;
- Only 20% of the heat energy is spent on heat;
- MaxGrow;
Orchid lamps should not get hot.
Please note:
- The base size can be standard E27. and smaller – E14;
- Warm colors (closer to yellow) - below 4000 K. During flowering;
- Daylight – 4000-6440K. Universal;
- Cold tones (close to blue) – more than 6500 K. During the growing season.
Luminescent
- Gases (often mercury), thanks to the coating of lamps with phosphor, provide the presence of ultraviolet rays: LB (white color);
- LD (daytime color);
- LDC (daytime color with improved color rendering).
- Philips;
- T8 (diameter 26 mm);
Halogen
- Metal halide devices are also called gas discharge devices. These are almost the same as incandescent lamps for plants. But improved and more expensive;
- Their shapes and color spectrum are varied. But for plants (and orchids), purchase special models;
Many amateur gardeners use lighting for orchids.
- White and blue models: Sunmaster Leuchtmittel Wuchs 600 W;
- Greenbud MH: 250 W;
- 400 W;
- 600 W.
Mercury gas discharge
- The principle of their operation is the same as that of fluorescent ones;
- But the marking is different;
Mercury gas discharges operate on the same principle as fluorescent ones.
- You need a glow temperature from 3,200 to 4,200 K;
- There are also sodium gas discharge lamps. Low and high pressure.
LED
- LED lamps are in greatest demand among orchid lovers;
- What attracts: Cost-effectiveness;
- Long service life;
- Environmental Safety;
- Resistance to temperatures, mechanical stress;
- No UV radiation.
LED phytolamps.
Of all types, experts consider the following lamps to be the most effective for orchids:
- For flowering: Sylvania 250 W, HPS-TS 400W;
- Osram Nav-N 250W, 400W, 600 W, 1000 W;
- Philips Son T-plus 400 W, 600 W;
- Greenbud HPS 400 W, 600 W, 1000 W;
- GIB Lighting Flower Specter HPS 250 W, 400 W,600 W.
- Sylvania Growlux 400W, 600W;
LED strips
Now on Aliexpress you can order a 1 meter long LED strip with different combinations of blue and red LEDs for a few dollars. To remove heat, it can be glued to an aluminum threshold for linoleum joints. You will also need a 12 Volt power supply, which it is advisable to order with a current reserve of at least 0.4A.
For some reason, the “flimsy” 100 mA power supplies offered by the seller stopped working after 2-3 weeks of use, after that I ordered a 0.4A power supply (it’s already so solid in the form of a rectangular box, like a laptop charger), I think it works with it there won't be any problems.
Lamp power and color temperature
Total power:
- for LED lamps of all LEDs 100-120 W per 1 square meter;
- for fluorescent lamps (T8, T5 (high power)) 180 W per 1 square meter.
The color temperature of lamps is expressed in Kelvin (K).
It is from this that we can determine the predominant light spectrum:
- 1500 – 3000 K
Lamps with these values are usually dark orange or dark red in color. Stimulates plant flowering
- 3000 – 3700 K
The lamps are yellow or neutral in color. They stimulate photosynthesis throughout all phases of plant growth.
- 3700 – 4000 K
The lamps have a warm and neutral color. Stimulate growth.
- 4000 K
Most lamps with this value are neutral white. Stimulates normal plant growth.
- 4000 – 5000 K
These lamps emit a light blue color. Stimulates the growth of leaves and stems of plants.
- 5000 – 8000 K
Lamps with this emission spectrum have a dark blue color and improve the development of leaves and stems of plants.
To illuminate orchids, it is better to use a glow temperature of about 3000 K.
The best option is to combine half the lamps with a temperature of 3000 K and half with 8000-10000 K (6500 K will also work).
Tips for choosing
In order to select a functional and reliable device to support the development of indoor and greenhouse crops, you need to take into account certain nuances
- The selection of a phytolamp should begin by calculating the area with which the device will work. It is also worth deciding on the frequency of lighting. A clear understanding of the requirements for the device will greatly facilitate its selection. As a rule, manufacturers indicate on their products information about the power of the product and the recommended operating area.
- Before purchasing, you should also decide at what distance the device will be placed relative to the plants. The best option would be to purchase phytolamps with the ability to regulate their location and height.
- Before purchasing lighting devices, it is also worth sorting existing crops based on the growing season.
- For small spaces, such as, for example, a window sill, you can opt for models with medium emitted power. As practice shows, indoor flowers will need fluorescent lamps with a glow temperature of about 6500 K. For greenhouses and conservatories in winter, high-performance and large lamps of a universal spectrum will be needed.
- To equip a room with lighting, you should give preference to one type of lighting fixture in order to create the most comfortable conditions for crop growth.
The need for lighting depending on the variety
When choosing a location for an epiphyte, in addition to the orientation of the windows, it is important to take into account the plant variety. For example:
- Vanda is a light-loving variety that needs high-quality lighting throughout the year. Lack of sunlight causes growth to slow down or stop. The plant does well on the south side with diffused, soft light.
- Cattleya - needs the longest daylight hours (up to 16 hours) and bright light. For growing this variety, well-lit window sills are recommended, but at the same time excluding direct sunlight. When placing Cattleya on the north side, it is necessary to use additional lighting.
- Phalaenopsis - prefers partial shade and grows well in any part of the room. In winter it needs additional lighting.
- Dendrobium develops fully in conditions with bright light, high levels of air humidity and moderate temperatures.
- Paphiopedilum is light-loving, but too sensitive to direct sunlight. A suitable place for growing it is the northern part of the room with additional lighting in spring, autumn and winter.
Light spectrum
The light spectrum is an important point in orchid breeding. In order for the plant to grow better, it is recommended to use devices that produce short-wave blue and long-wave red rays. To create such a light spectrum, a special device operating in combined mode is required. You can also purchase two devices that operate in red and blue modes, respectively.
It is worth remembering that the light spectrum changes throughout the day. To improve the synthesis of chlorophyll in green leaves, which is required for active growth and development, it is necessary that red rays hit the plant only in the dark. At other times, the flower needs blue rays.
Why is this necessary?
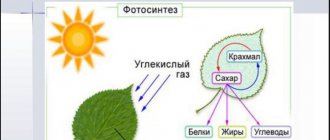
First, let's determine why plants need light. Inside the green leaves of the orchid, photosynthesis occurs, carried out by the green pigment - chlorophyll. From the solar spectrum, it absorbs blue and red light using chlorophyll A and B.
Chlorophyll B absorbs sunlight - long red wavelengths of 642 nm. and short blue at 453 nm. Chlorophyll A processes energy obtained at long red waves of 662 nm. and short blue ones from 410 to 430 nm. Light absorption is not uniform throughout the day - blue light is absorbed almost all day, and red light is absorbed in the morning and evening. In winter or in a poorly lit apartment, it is almost impossible to achieve such lighting. Therefore, lamps are required for orchids grown at home.
Important! When choosing a lamp for your orchid, make sure it contains both blue and red light.
Red helps flowering, and blue helps the growth of foliage, but only combined lighting will lead to the harmonious development of the flower. We will talk in more detail about what phytolamps are needed for orchids and how to choose them in the corresponding section.
Useful tips
Growing under full artificial light
It is not always possible to find a sufficiently lit place for an orchid. There are many examples of growing them entirely under artificial light.
What is important to decide:
- Set day and night temperature modes. They are important for many orchids. Especially for flowering; Orchid lighting option.
- Provide other conditions for the selected type of orchid: Humidity;
- Air circulation;
- And be sure to the power of the lamp and its distance from the flowers.
Solar lamp
It’s worth looking at such lamps in reality. Beauty in the garden becomes special. In the evening and at night. 5 pcs for 370 UAH. Great for the garden and home!
And the usefulness for orchids is a separate topic. And here we are not talking about frugality. About usefulness. For orchids, they do not provide the best spectrum for growth and flowering (red and blue). But you can count.
Why do you need backlighting?
Plants need sunlight to grow and develop. This fact is well known to everyone from high school biology courses. UV rays are an essential participant in the process of photosynthesis. To find out what kind of lighting orchids need, you need to understand what this process is.
Special green pigments are responsible for its implementation - chlorophylls of type B and A. The first type (B) absorbs long waves of the red spectrum and short blue ones. The second type of chlorophyll (A) processes absorbed energy, directing it to cell growth.
Interesting! The red spectrum of light is responsible for the flowering of the plant, and the blue one promotes the growth of green mass (foliage). Combining them significantly accelerates the growth and normal development of the culture.
In winter or when the flower bed is located far from natural light, a significant slowdown in the process of photosynthesis is observed.
Additional lighting for orchids, organized in the apartment, can solve this problem. However, when choosing, the grower must pay attention not only to the presence of radiation in the lamps in the red and blue spectrum, but also to other technical and operational characteristics of the devices.
Calculation of drivers and choice of basis
Linear LED Driver
The power supply is an essential part of the lamp. It equalizes the output voltage and supplies the LEDs with optimal power.
The documentation for the tape indicates the value of the voltage drop at different current levels. This value must be multiplied by the number of diodes. The optimal number of drivers is selected from the resulting parameter.
Recommendations to help with installation and connection:
- The best driver option is 50 W. More powerful devices will heat up and cost more. In terms of current, the optimal choice of source is 600 mA.
- During driver calculations, the actual power of the LEDs should be taken into account, not the maximum power. It is calculated as the current of the source used multiplied by the voltage drop.
When choosing a driver, you need to pay special attention. Without this element, normal operation of the phytolamp is impossible.
Any material can be used as the surface of the lamp. Phytolamps are often made from plywood or boards, but in this case it is necessary to consider a cooling system. It is better to take aluminum - then the heat will be removed from the surface and the device will last longer.
How to choose a lamp
Lamps for indoor plants ensure their active growth, especially in the autumn-winter period. Some representatives of the flora need longer daylight hours, so you need to turn on the lamps in the evening. For this purpose, different lighting elements are used: filament lamps, fluorescent, sodium, LED. They all have both their pros and cons.
Incandescent lamp
Incandescent lamps are rarely used for indoor flowers. This is due to the fact that they have high heat transfer and emit red, orange, and infrared rays. Under the influence of such light, representatives of the flora get burned, their sprouts become greatly elongated and also become thinner. Another disadvantage of filament lamps is their short service life.
Luminescent
Tubular light bulbs for indoor flowers with a white glow can be used for illumination, but the red waves in their spectrum are quite weak. They hardly heat up, but over time their light output decreases.
For lighting it is better to use phytoluminescent lamps. They are economical, compact, durable and safe. They have earned great popularity due to their selective spectrum and low heat transfer.
When using reflectors, the efficiency of tubular lamps increases by 25%.
Gas discharge
Sodium lamps emit bright light, last a long time, and are highly economical. However, they are more often used in greenhouses, as they are very bright (from 15,000 lux). There are not enough blue waves in their spectrum, so they are often combined with luminescent ones. Such devices are quite large, so they can illuminate a large area. The disadvantages include the high cost and the presence of mercury vapor in the flask.
LED
LED lamps are the best option for indoor flowers. They have high efficiency, energy efficiency, and durability (up to 50,000 hours). The dimensions of the LEDs are minimal, so they can be placed in hard-to-reach places (shelves, niches). They hardly heat up and are environmentally friendly. LED lamps emit red, blue, and orange light, which allows you to regulate the growth of indoor plants. Their only drawback is their high cost, but this is soon compensated for by saving electricity.
What kind of lamp is needed?
Lighting manufacturers offer a wide range of different lamps that are suitable for additional lighting of green spaces. When choosing, you should take into account the operating principle of the device, cost and other performance characteristics. Among the most popular:
- Metal halide lamps. In the assortment of such products, you need to look for those that are intended for growing plants in apartment conditions. The advantages lie in high-quality radiation and a wide range of shapes and sizes.
- Fluorescent lamp. This is a compact product that uses gases to produce UV rays. The surface of the lamp is coated with phosphor. For plants you need to choose shades numbered 33 and 840. Marking can be of several types: LB, LD or LDC.
- Energy saving lamps. These types of lamps are widely used for home lighting. Among the advantages are the relatively low price, short circuit protection and long service life. The distance from the lighting fixture to the leaves should be at least 5 cm.
- Mercury gas discharge lamps. According to some characteristics, these products are similar to luminescent ones. The glow temperature of such devices should vary between 3200–4200°K.
- LED lamps. Such options are often called universal. In the assortment you can choose a phytolamp for orchids that works in one color spectrum. In addition, combined devices are presented that allow you to change the ratio of red and blue radiation.
If only 1-2 plants need lighting, then purchasing specialized lighting is irrational. In this case, it is worth purchasing a standard LED lamp.
Other types of lamps
The closer to the North Pole you live, the more necessary lighting is for orchids. In the tropics, such beauties do without artificial lighting.
Incandescent
- What can a regular 100 W incandescent light bulb do? It emits: Light about 2%;
- Almost 98% heat.
Incandescent lamp.
Placing directly with a lamp may burn orchid leaves; Remove further - there will not be enough light; It's better to turn it off completely.
Ultraviolet
An ultraviolet lamp may come in handy... For other purposes. Warming up the back...
UV lamp for reptiles from Aliexpress.
Ultraviolet light can be:
- In the range from 315 to 400 Nm. It is not enough for photosynthesis. Harmless to plants;
- Range from 280 to 315 Nm. Such rays disrupt plant DNA;
- Range from 100 to 280 Nm. Plants stop growing. They may die.
Should I experiment with such lamps with orchids? I wouldn't recommend it. If there are others. Obvious ones.
With your own hands
Installing the lighting yourself will be much cheaper. How will specialists do this?
It all depends:
- How many orchids need to be provided with lighting;
- What do you have available?
- Basic knowledge of handling electrical appliances;
- Availability of funds for this;
- At one time, amateur radio was very popular. They even made stereo tape recorders with a soldering iron. And now there are such people. There are fewer of them. But the conditions are better for creative thought.
Here are examples:
In addition to lighting, the orchid must be provided with humidity and air circulation.
I really wanted to offer such phytolamps from domestic ones... Maybe we haven’t had time to turn in this direction yet? But the direction is very promising!!!
The Green Power phytolamp is considered one of the cheapest.
But China is keeping up. And many phytolamps are offered by them. And quite high quality:
- Green Power phytolamp (made in China). Power from 5 to 54 W. Cost from 130 to 1300 UAH;
- LED phytolight SL-036W IP65 linear up to 50,000 hours. Power 2x18. With a 2 to 4 ratio of blue to red. And it only consumes 9 watts.
You can look for the best price. But for a long time. It's hard to decide right away. The price may be small. But I remember something else. Cheap cheese is always in a mousetrap. So it’s not just the price that needs to be taken into account. But there are other criteria too. Their effectiveness comes first.
Decorative tabletops
Many dissertations are written about decorative lamps. The variety on the market leaves no one indifferent.
For an orchid, other characteristics of such lamps are more important:
- Is it possible to use phytolamps for illumination in them? And what? It turns out you can;
- Your imagination may even lag behind the proposal. Just look. And if you wish, you can find addresses. And check prices.
Smart people who know a lot about orchids have created lamps in the shape of orchids:
- They look simply amazing;
- And they cost no less than natural ones. And somewhere on the level. And sometimes higher;
- Caring for them is much easier! (don’t forget the location of the outlet);
- But you have to see it! It’s easy to confuse them with natural ones.
If you look closely at the bud, you can see a lamp.
Are you an amateur or a pro?
If you have only one orchid, which you may have been given as a gift, or you accidentally, in an emotional outburst, bought it at a sale, then you are definitely an amateur. You are just getting used to caring for an exotic beauty. And, most likely, you have one of the most unassuming orchids, like phalaenopsis.
To provide a bright and comfortable winter for unpretentious representatives of this kind, you can use ordinary housekeeper lamps, fluorescent tubes of the following markings:
- LB (luminescent, white color)
- LD (luminescent, daylight)
- LDC (luminescent, daytime color, with improved color rendering)
This is quite enough for amateur floriculture.
If you have collected a fairly decent collection of orchids, consisting of different genera, then you can already be called a professional in growing orchids.
And if you want to achieve winter flowering from demanding light-loving species, then you will need competent and more powerful lamp equipment than ordinary “housekeepers”. We are talking about special lamps suitable for growing plants, or, as they are also called, phytolamps. They use red and blue light waves to influence growth and flowering.
Lamp installation options
There are several ways to mount lighting fixtures:
- Table lamp for orchids or lamp. This option should be used in cases where the orchid pot is on a windowsill, shelf or table. To speed up the process of photosynthesis, it is worth installing a separate small lamp above each plant. In this case, you need to ensure that the main flow of light is directed not at the buds, but at the leaves.
- Pendant lamps. If one light source will be used for several pots, then it is better to mount it a little higher. An example is a design in which the lamp is mounted on a horizontal crossbar or on a vertical stand.
- Fastening to furniture. You can choose this method in cases where pots with orchids (and other plants) are installed on shelves. Then the top shelf will become a good platform for mounting lamps that illuminate the lower tier.
Great choice
There are many different light sources on the market now. To help you figure out which orchid lamps to buy, we've put together an overview table describing each type.
A phytolamp for orchids is actually very important for plants, since it plays an important role in their development and subsequent flowering. Often the gardener does not have the opportunity to transfer the entire home oasis to the windowsill located near the window on the south side of the house. Also, plants kept in an apartment see very little light even on a clear day in summer, and besides, on the other side of the window, nearby houses or trees successfully cover it. That is why a variety of lamps have been made that can compensate for the lack of sunlight for house plants.
However, how to decide on the type of lamp to satisfy all the needs of such a capricious exotic plant as an orchid? To do this, please review the information provided below.
Recommendations
The huge variety of lamps suitable for organizing additional illumination of orchids can lead to difficulties when choosing a device. LED and fluorescent lamps are quite popular among those who like to grow these tropical plants. It is worth noting that such devices are suitable both for those who have been growing orchids for a long time, and for those who have recently become the owner of these plants.
For those who have only 1-2 orchids and do not plan to purchase such plants in the future, experts recommend limiting themselves to purchasing an energy-saving light bulb. Such a purchase will cost the gardener very little.
See below for more details.
Which one to choose – red or blue?
When looking for an orchid lamp, you may be asked to buy either a blue or a red one. Which one to choose? The answer will be: none of them separately, but only together. And you can also add a regular fluorescent lamp to them. Now you will understand why.
If you use only red light to illuminate orchids, which has a beneficial effect on flowering, then they will bloom more often; the number of flower stalks and the duration of flowering will increase, which, of course, cannot but rejoice.
But at the same time, new shoots and leaves will become longer, and all plant tissues will become much thinner. And this can lead to serious deformations; the orchid can bend under the weight of its weight.
If you grow orchids only under blue light, the leaves, on the contrary, become more compact, thick and fleshy; the number of side shoots may increase; The plant tissues are painted a rich green color.
Therefore, in order to provide your pets with the entire necessary spectrum, so that both the green parts and flower stalks develop evenly, it is recommended to use both lamps. And in the conditions of an orchidarium, it is necessary to turn on regular daylight lighting for an additional 1-2 hours.
You can choose one of two backlight modes:
Option 1. Turn on the red light in the morning and evening, and the blue light during the day (in the orchidarium, if there is no natural light, it is recommended to additionally turn on the daylight lamp for 1 hour in the morning and evening).
Flower needs at different times of the year
The greatest need of orchids at home is additional lighting, which is necessary from mid-autumn to early spring. During the rest of the year, most types of orchids have enough natural light. However, for this, the windows of the house must be directed towards the Southeast side of the globe. Otherwise, lamps may be required during the rest of the year.
In the spring-autumn period, lamps can be used as additional lighting, and after dusk. In this case, there is absolutely no need to keep them turned on throughout the day.
In the natural environment, the duration of daylight hours for orchids is usually more than 10 hours, or more precisely from 10 to 14 hours, therefore lighting devices for them should not be used longer than this time.
In this case, the lighting intensity is selected according to the species to which the orchid belongs.
It is quite easy to determine this yourself by paying attention to the shape of the leaf. Plants with narrow, pointed leaves require the most light.
Orchids that have thick leathery leaves and pseudobulbs are less demanding in this regard.
Medium light levels are suitable for orchids with thin leaves and pseudobulbs. And those plants that do not have pseudobulbs, but have wide and delicate leaves, do not require additional lighting at all. In addition, these exotic plants tend to adapt to new conditions, so with a slight lack of lighting they will not lose their ability to flower.
Also, do not forget that excess light also negatively affects the plant, as does its deficiency. An orchid will not be able to take in more than it needs, and excess energy leads to overheating and subsequent death of the flower.
Light duration for orchids
You need to focus on the length of natural daylight.
The total duration of daylight for orchids is no less than 10 and no more than 14 hours a day.
The length of daylight hours should be increased by illuminating the orchids in the morning and evening hours.
The lamps can be turned on all day long if it is cloudy outside or there is not enough light in the room.
Important! Orchids should not at night . Disruption of biorhythm will negatively affect the life of plants, even to the point of their death.
↑ How to enhance lighting yourself
The simplest and cheapest way to enhance natural light is to cover the walls and the window sill itself with foil. This shiny material reflects heat and light well. You just need to take into account that foil is effective only in sunlight. If the day is rainy or cloudy, the foil will not provide reflection.
Foil has several advantages when used as a reflector:
- the level of solar illumination increases by 20-30%;
- heat and light are distributed evenly across all plants in the container. Usually the corners of the window sill are poorly illuminated by lamps, but with foil there is no such problem;
- the appearance of seedlings occurs evenly, the shoots grow evenly, without bending the stem.
To arrange such lighting you will need foil, masking tape and scissors. The foil is evenly distributed over the window sill and its walls, secured with tape.
Lighting organization
In the area where such flowers grow in the wild, daylight hours reach 10-13 hours. This indicator is optimal for growth and flowering, so you should focus on it when organizing lighting at home. At the same time, several other factors should not be overlooked:
- Orientation of the window in the room. If the room faces south, then in most cases there will be enough sun for flowers. Windows facing east, west or north do not provide the amount of light that flowers require.
- Light level. In shaded rooms with poor lighting, orchids will always need to have lights turned on (at least briefly).
- Seasonality. In rooms facing south, artificial lighting can be turned on only in the winter season; on the eastern and western windows of the house, moderate additional light is required in the twilight. The north side requires constant use of the lamp.
- Orchid variety. Not all varieties of these flowers have the same requirements for the amount of ultraviolet light. If the leaves of the plant are long and narrow, this indicates a light-loving plant. Green spaces with dense, wide leaves are classified as shade-loving. You should connect a lamp for them only if the plant looks lethargic and sick.
How to organize lighting?
When is it needed?
From October to March, all orchids need lighting, regardless of the location of the windows. Located on the north side - almost all year round. On the eastern and western sides during twilight, a little “additional lighting” is needed in spring and autumn. You can also provide additional light to weakened plants.
How to choose a device?
There are a large number of lamps on the market. The following are suitable for growing orchids:
- Special energy-saving lamps produced in the blue and red spectrum. Manufacturers guarantee that only 20% of the energy is converted into heat by the device, but they should not be placed close to the leaves. The minimum distance is 3 cm.
- Fluorescent lamps. Using gases such as mercury, they produce ultraviolet light, which is made visible by coating the lamp with phosphor. For orchids, devices with shades 33 and 840 are suitable.
- Metal halide lamps, also called gas discharge lamps. These devices can be of any shape; special models for growing plants are also available.
- Mercury gas discharge lamps work in the same way as fluorescent lamps, but have different markings. Choose those whose glow temperature is in the range from 3,200 to 200 K.
- LED lamps, otherwise known as light-emitting diodes, are considered optimal for floriculture. In stores you can find combination models with red and blue light with a ratio of 8/1 or 5/1 red and blue.
So what is the best lamp to illuminate orchids?
Special phytolamps that emit light at the required intensity and wavelengths are ideal. The most popular are fluorescent and LED. These are the best options for both amateurs and experienced gardeners. If you are a complete beginner, you can buy a regular energy-saving light bulb, but you shouldn’t expect any special effect from it, so it’s still better to install an inexpensive LED lamp.
If you are an amateur and you only have one or two flowers, there is no need to spend money on a special paw; an energy-saving one will suffice. And to keep a large number of exotic orchids you will need professional lighting.
What color should the rays be?
Light with long red and short blue waves is preferred for orchids. You need to buy either one lamp that combines both of these spectra, or separate ones - red and blue. In the second case, the blue one is turned on throughout the day, and the red one at dusk.
Installation
There are several options for lighting orchids:
- For a small window sill, an office lamp with a screw mount or a clothespin is suitable.
- For a dozen low orchids, compact fluorescent lamps located above the foliage are suitable (photosynthesis practically does not occur in flowers, there is no point in lighting them). You can attach them to the underside of a shelf or a window crossbar. Help! It is better to combine the first and second types of lamps with reflectors - this way more light will fall on the flowers. For this purpose, you can use not only special reflectors, but also an ordinary mirror.
- If you have a winter garden, you will need high-quality ceiling lighting with gas-discharge lamps of at least 250 W of power.
Below is a visual video about lighting for an orchid using pendant lamps:
Duration
Orchids are accustomed to long daylight hours, on average up to 12 hours. Specific lighting standards are individual and depend on the orchid variety. The minimum time frame is 10 hours, the maximum is 16.
Effect on the plant
Properly installed lighting has a positive effect on the plant, causing the growth of green mass and increasing flowering. In winter, artificial light will prevent the plant from falling into a dormant state, which will cause it to bloom more often.
Errors in organizing lighting and their consequences
Novice amateur gardeners often make mistakes when organizing lighting that affect the development of plants. Most often what happens:
- incorrect selection of lamps;
- violation of the emission regime of the red and blue spectrum of light;
- artificial extension of daylight hours;
- violation of basic agricultural practices.
So, if exposed to red radiation for too long, the quality of the orchid’s flowering will improve, but the peduncle itself will suffer. It will become thinner to such an extent that any careless movement will damage it. An abundance of blue light will enhance the growth of green mass, but will not allow the plant to bloom.
Important! You can understand that an orchid receives light in abundance by the state of its foliage. The plates are painted in a light reddish tint. The dark green color of the foliage with a blue tint indicates a lack of ultraviolet radiation.
Flower growers should also remember the basic agrotechnical requirements for orchids: high humidity, loose soil, watering regime and optimal temperature from 10 to 30°C.
Types of phytolamps
As we have already said, fluorescent lamps began to be used earlier than others to illuminate indoor plants and seedlings. Today, manufacturers have learned to change their luminescence spectrum in the range optimal for photosynthesis.
The positive qualities of these devices are low price, high light output and energy efficiency. Weaknesses include a low resource (no more than 10,000 hours) and a rapid decrease in glow strength as the lamp ages. Taking this into account, it is most profitable to install this type of lighting in greenhouses for short-term (3-4 weeks) illumination of seedlings located over a large area.
Fluorescent phytolamps generate lilac-pink light. It is harmful to vision and can cause headaches. Therefore, in residential areas they should be used with a mirror reflective screen.
Energy-saving phytolamps (housekeepers)
A modern type of fluorescent lamps. They differ from their predecessors in their compact size, long service life (15,000 hours), the presence of a built-in choke and a convenient e27 “bulb” socket.
However, experienced gardeners are not happy with them. They prefer linear fluorescent phytolamps.
They explain their choice by the fact that housekeepers have lower light output due to the tightly twisted glass tube (self-darkening effect).
Sodium phytolamps
Economical, durable, characterized by high power and stable luminous flux. The orange-yellow glow they generate is beneficial to plants and does not irritate the eyes. Therefore, this type of lamps can be used not only in greenhouses, but also in apartments. For home use (additional lighting of seedlings and flowers on the windowsill), one lamp with a power of no more than 100 W is sufficient.
In rooms where there is no sunlight, sodium lamps are used together with fluorescent lamps (LB or LBT brands).
The disadvantages of this type of lamps include the high cost of ballasts. When using sodium lamps, you need to be careful, since their bulbs get very hot (up to +300C) and can explode if water drops hit the surface.
Induction lamps
The principle of operation is similar to luminescent (an electric discharge in a glass tube initiates the glow of the phosphor). They differ significantly in design. The induction lamp has no internal electrodes, which significantly increases its service life (at least 60,000 hours). In terms of a 12-hour operating mode, this is about 20 years.
The brightness of a lamp with an induction coil decreases minimally over time (about 5%). It is not afraid of power surges and does not flicker during operation. The absence of strong heating of the bulb allows you to place induction lamps in close proximity to the plants, increasing the lighting intensity.
Their color rendition is as close as possible to the spectrum of sunlight. Therefore, induction lamps can be used without combining with other sources of phytolight. The main disadvantage of these lamps is their high cost.
LED phytolamps
When creating phytolights, designers did not ignore LEDs. They have many important advantages. Consuming a minimum of energy, LEDs generate powerful radiation. Its spectral composition is selected quite simply (by installing a certain number of blue and red diodes).
LED lamps for plants differ from other phytolight sources in their long service life (about 50,000 hours) and stable radiation characteristics, which are little dependent on the period and operating conditions. The heating of the LED module is low, which eliminates the risk of burning plants. Compact placement in the same block with the ballast lamp, the use of a standard “bulb” base simplifies and reduces the cost of their use as lighting.
How to organize plant lighting at home?
To properly organize the illumination of an orchid, you need to take into account a number of subtleties. First of all, it is necessary to choose the right device that emits rays of the desired light spectrum. It is necessary to consider when the backlight is required and for what period it will need to be turned on.
When should you highlight?
The orchid requires additional lighting starting in mid-autumn, when the days become so short that natural light is not enough for the orchid.
Starting in October, you can turn on the backlight at approximately 7 a.m. and turn it off at approximately 6 p.m. In summer, weakened orchids need lighting.
Which phytolamp to choose?
Many types of devices can be used to illuminate orchids. To create additional lighting, the following types of lamps can be used:
- energy saving;
- luminescent;
- gas discharge;
- mercury gas discharge;
- LED
Now on sale there are special energy-saving lamps that emit rays in red and blue light, necessary for orchids. At the same time, only 20% of the energy is processed by the device into heat, so the risk of leaf damage is minimal.
The minimum distance from the light source to the plant is 3 cm. Fluorescent lamps work due to the interaction of electric current and gas. Devices with shades 22 and 840 are suitable for illuminating orchids.
To grow plants, you must use only special models of gas-discharge lamps. If you plan to organize the backlight using mercury gas-discharge lamps, it is better to choose those devices whose glow temperature is in the range from 3,200 to 200 K.
Among LEDs, the most suitable for backlighting are combined models that combine the red and blue spectrum in a ratio of 8/1 or 5/1.
Color and spectrum of the device
When creating an additional lighting system for orchids, it is important to consider that these races require both long red and short blue waves. Thus, it is necessary to purchase a device that combines both spectrum data
How to install the device above a flower?
Getting the lighting right is not difficult. If the orchid is small and is constantly located on the windowsill, you can use an office lamp equipped with a clothespin or screw mount. A light bulb with the required spectrum characteristics is inserted into the device.
When growing up to 10 small orchids on one windowsill, you can use compact fluorescent devices. They are placed on racks that are installed on both sides of the window sill. To illuminate the winter greenhouse, it is recommended to install high-quality ceiling lighting and install gas-discharge lamps.
How much light do you need?
Orchids require long hours of daylight to grow and bloom normally. In Russia, most of the autumn, winter and spring weather is cloudy, so the plant will need lighting for 10-12 hours.
Why do orchids need lighting?
The length of daylight hours plays a key role in the proper development of orchids and their ability to bloom regularly.
Read more about lighting here.
Backlighting is used to extend daylight hours on window sills.
What does sufficient illumination mean? Each plant has its own. For orchids, the optimal indicator is in the range from 10 thousand to 30 thousand lux .
This indicator depends on the area where orchids grow:
- for orchids growing in open areas , 30 thousand lux of daylight is required;
- for those growing in partial shade - at the level of 15 thousand lux .
In our latitudes, the intensity of lighting on the street:
- in summer reaches 50 thousand -100 thousand lux,
- in autumn does not exceed 30 thousand lux,
- in winter it is at a level of about 5 thousand lux.
If the orchid is located at a distance of more than 1 m from the window , then we should no longer talk about lighting, but about light culture .
In the back of the room, lamps act as the main source of light and are responsible for the full development cycle of orchids.
There are situations when an orchid is brought home with long, fleshy leaves , and after several months the new leaves grow shorter and more rounded.
The fact is that the light intensity has changed (there is more light than before) and the orchid no longer needs to grow long leaves to catch more light. This is a normal reaction!
This also happen in the same window . In winter and autumn it is a little dark, the leaves grow longer , and in summer and spring there is more light, so the length of the leaves is shortened and the shape changes.